Obesity and mortality of COVID-19. Meta-analysis
- PMID: 32660813
- PMCID: PMC7346803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.orcp.2020.07.002
Obesity and mortality of COVID-19. Meta-analysis
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to Obesity a nd Mortality of COVID-19.Meta-analysis [Obesity Research & Clinical Practice 14/4 (2020) 295-300].Obes Res Clin Pract. 2021 Jan-Feb;15(1):100. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2020.12.008. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 33563391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a global disease with at least 2.8 million people dying each year as a result of being overweight or obese according to the world health organization figures. This paper aims to explore the links between obesity and mortality in COVID-19.
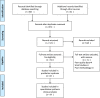
Methods: Electronic search was made for the papers studying obesity as a risk factor for mortality following COVID-19 infection. Three authors independently selected the papers and agreed for final inclusion. The outcomes were the age, gender, body mass index, severe comorbidities, respiratory support and the critical illness related mortality in COVID-19. 572 publications were identified and 42 studies were selected including one unpublished study data. Only 14 studies were selected for quantitative analysis.
Results: All the primary points but the gender are significantly associated with COVID-19 mortality. The age >70, [odd ratio (OR): 0.17, CI; 95%, P-value: <0.00001], gender [OR: 0.89; CI: 95%, P-value: 0.32], BMI > 25 kg/m2 [OR: 3.68, CI: 95%, P-value: <0.003], severe comorbidities [OR: 1.84, CI:95%, P-value: <0.00001], advanced respiratory support [OR: 6.98, CI: 95%, P-value: <0.00001], and critical illness [OR: 2.03, CI: 95%, P-value: <0.00001].
Conclusions: Patients with obesity are at high risk of mortality from COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: Body mass index; COVID-19; Intensive care unit; Mortality; Obesity; Total body weight; World Health Organization.
Copyright © 2020 Asia Oceania Association for the Study of Obesity. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Zhou X., Ye Y., Tang G., Zhou X. Obesity and infection, accompanying phenomenon or causal association? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24:668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

