A Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Interferon β-1a in Treatment of Severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32661006
- PMCID: PMC7449227
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01061-20
A Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Interferon β-1a in Treatment of Severe COVID-19
Abstract
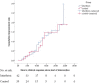
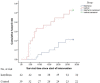
To the best of our knowledge, there is no published study on the use of interferon β-1a (IFN β-1a) in the treatment of severe COVID-19. In this randomized clinical trial, the efficacy and safety of IFN β-1a were evaluated in patients with severe COVID-19. Forty-two patients in the interferon group received IFN β-1a in addition to the national protocol medications (hydroxychloroquine plus lopinavir-ritonavir or atazanavir-ritonavir). Each 44-μg/ml (12 million IU/ml) dose of interferon β-1a was subcutaneously injected three times weekly for two consecutive weeks. The control group consisted of 39 patients who received only the national protocol medications. The primary outcome of the study was time to reach clinical response. Secondary outcomes were duration of hospital stay, length of intensive care unit stay, 28-day mortality, effect of early or late administration of IFN on mortality, adverse effects, and complications during the hospitalization. Between 29 February and 3 April 2020, 92 patients were recruited, and a total of 42 patients in the IFN group and 39 patients in the control group completed the study. As the primary outcome, time to the clinical response was not significantly different between the IFN and the control groups (9.7 ± 5.8 versus 8.3 ± 4.9 days, respectively, P = 0.95). On day 14, 66.7% versus 43.6% of patients in the IFN group and the control group, respectively, were discharged (odds ratio [OR], 2.5; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05 to 6.37). The 28-day overall mortality was significantly lower in the IFN than the control group (19% versus 43.6%, respectively, P = 0.015). Early administration significantly reduced mortality (OR, 13.5; 95% CI, 1.5 to 118). Although IFN did not change the time to reach the clinical response, adding it to the national protocol significantly increased discharge rate on day 14 and decreased 28-day mortality. (This study is in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials under identifier IRCT20100228003449N28.).
Keywords: COVID-19; clinical response; interferon; mortality.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply to Dorgham et al., "Considering Personalized Interferon Beta Therapy for COVID-19".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Mar 18;65(4):e00083-21. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00083-21. Print 2021 Mar 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33558288 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Considering Personalized Interferon Beta Therapy for COVID-19.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Mar 18;65(4):e00065-21. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00065-21. Print 2021 Mar 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33558300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. 2020. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 395:1054–1062. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, Huang H, Zhang L, Zhou X, Du C, Zhang Y, Song J, Wang S, Chao Y, Yang Z, Xu J, Zhou X, Chen D, Xiong W, Xu L, Zhou F, Jiang J, Bai C, Zheng J, Song Y. 2020. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med 180:e200994. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwl4v4BRDaARIsAFjATPmRcsB7VPlJAxJMh.... Accessed 6 July 2020.
-
- Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, Ruan L, Song B, Cai Y, Wei M, Li X, Xia J, Chen N, Xiang J, Yu T, Bai T, Xie X, Zhang L, Li C, Yuan Y, Chen H, Li H, Huang H, Tu S, Gong F, Liu Y, Wei Y, Dong C, Zhou F, Gu X, Xu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li H, Shang L, Wang K, Li K, Zhou X, Dong X, Qu Z, Lu S, Hu X, Ruan S, Luo S, Wu J, Peng L, Cheng F, Pan L, Zou J, Jia C, Wang J, Liu X, Wang S, Wu X, Ge Q, He J, Zhan H, Qiu F, Guo L, Huang C, Jaki T, Hayden FG, Horby PW, Zhang D, Wang C. 2020. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med 382:1787–1799. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous