Rab27a co-ordinates actin-dependent transport by controlling organelle-associated motors and track assembly proteins
- PMID: 32661310
- PMCID: PMC7359353
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17212-6
Rab27a co-ordinates actin-dependent transport by controlling organelle-associated motors and track assembly proteins
Abstract
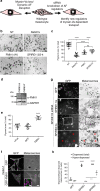
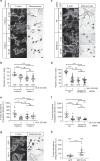
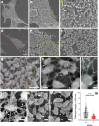
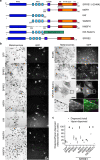
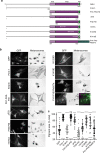
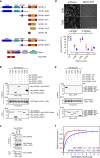
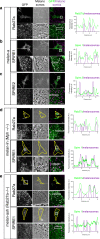
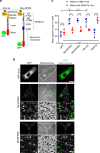
Cell biologists generally consider that microtubules and actin play complementary roles in long- and short-distance transport in animal cells. On the contrary, using melanosomes of melanocytes as a model, we recently discovered that the motor protein myosin-Va works with dynamic actin tracks to drive long-range organelle dispersion in opposition to microtubules. This suggests that in animals, as in yeast and plants, myosin/actin can drive long-range transport. Here, we show that the SPIRE-type actin nucleators (predominantly SPIRE1) are Rab27a effectors that co-operate with formin-1 to generate actin tracks required for myosin-Va-dependent transport in melanocytes. Thus, in addition to melanophilin/myosin-Va, Rab27a can recruit SPIREs to melanosomes, thereby integrating motor and track assembly activity at the organelle membrane. Based on this, we suggest a model in which organelles and force generators (motors and track assemblers) are linked, forming an organelle-based, cell-wide network that allows their collective activity to rapidly disperse the population of organelles long-distance throughout the cytoplasm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Goode, B. L., Drubin, D. G. & Barnes, G. Functional cooperation between the microtubule and actin cytoskeletons. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.12, 63–71 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Langford GM. Actin- and microtubule-dependent organelle motors: interrelationships between the two motility systems. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995;7:82–88. - PubMed

