Impaired mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation limits the self-renewal of T cells exposed to persistent antigen
- PMID: 32661364
- PMCID: PMC7442749
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0725-2
Impaired mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation limits the self-renewal of T cells exposed to persistent antigen
Abstract
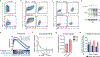
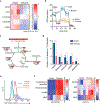
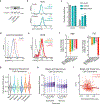
The majority of tumor-infiltrating T cells exhibit a terminally exhausted phenotype, marked by a loss of self-renewal capacity. How repetitive antigenic stimulation impairs T cell self-renewal remains poorly defined. Here, we show that persistent antigenic stimulation impaired ADP-coupled oxidative phosphorylation. The resultant bioenergetic compromise blocked proliferation by limiting nucleotide triphosphate synthesis. Inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in activated T cells was sufficient to suppress proliferation and upregulate genes linked to T cell exhaustion. Conversely, prevention of mitochondrial oxidative stress during chronic T cell stimulation allowed sustained T cell proliferation and induced genes associated with stem-like progenitor T cells. As a result, antioxidant treatment enhanced the anti-tumor efficacy of chronically stimulated T cells. These data reveal that loss of ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation limits T cell proliferation and effector function during chronic antigenic stimulation. Furthermore, treatments that maintain redox balance promote T cell self-renewal and enhance anti-tumor immunity.
Figures


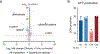
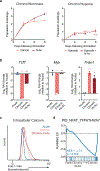
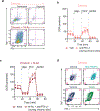
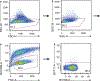
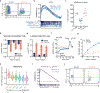
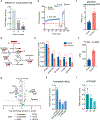
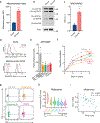
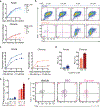
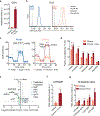

Comment in
-
Mitochondrial Damage and the Road to Exhaustion.Cell Metab. 2020 Dec 1;32(6):905-907. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.004. Cell Metab. 2020. PMID: 33264601
References
-
- Hanahan D & Weinberg RA Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui I et al. Intratumoral Tcf1(+)PD-1(+)CD8(+) T Cells with Stem-like Properties Promote Tumor Control in Response to Vaccination and Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Immunity 50, 195–211 e110 (2019). - PubMed
Methods-only references
-
- Anders S et al. Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and Bioconductor. Nature protocols 8, 1765–1786 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

