ACE2, the Receptor that Enables Infection by SARS-CoV-2: Biochemistry, Structure, Allostery and Evaluation of the Potential Development of ACE2 Modulators
- PMID: 32663362
- PMCID: PMC7405163
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202000368
ACE2, the Receptor that Enables Infection by SARS-CoV-2: Biochemistry, Structure, Allostery and Evaluation of the Potential Development of ACE2 Modulators
Abstract
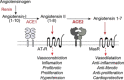
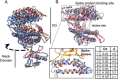
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the human receptor that interacts with the spike protein of coronaviruses, including the one that produced the 2020 coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Thus, ACE2 is a potential target for drugs that disrupt the interaction of human cells with SARS-CoV-2 to abolish infection. There is also interest in drugs that inhibit or activate ACE2, that is, for cardiovascular disorders or colitis. Compounds binding at alternative sites could allosterically affect the interaction with the spike protein. Herein, we review biochemical, chemical biology, and structural information on ACE2, including the recent cryoEM structures of full-length ACE2. We conclude that ACE2 is very dynamic and that allosteric drugs could be developed to target ACE2. At the time of the 2020 pandemic, we suggest that available ACE2 inhibitors or activators in advanced development should be tested for their ability to allosterically displace the interaction between ACE2 and the spike protein.
Keywords: ACE2; allostery; coronavirus; drug development; protein dynamics.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhanced Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Receptor by Distal Polybasic Cleavage Sites.ACS Nano. 2020 Aug 25;14(8):10616-10623. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c04798. Epub 2020 Aug 4. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32806067
-
Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2.Nature. 2020 May;581(7807):221-224. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32225175 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor.Nature. 2020 May;581(7807):215-220. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32225176
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 12;10(16):7448-7464. doi: 10.7150/thno.48076. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32642005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: Potential therapeutic targeting.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;884:173455. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173455. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32745604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological therapies and drug development targeting SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022 Dec;68:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022. PMID: 36266222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 biology and variants: anticipation of viral evolution and what needs to be done.Environ Microbiol. 2021 May;23(5):2339-2363. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15487. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33769683 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Nonfunctional Ras.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 Feb 18;28(2):121-133. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.12.012. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33440168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2-Based Biosensing Modalities and Devices for Coronavirus Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;12(11):984. doi: 10.3390/bios12110984. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBD-2 binds SARS-CoV-2 RBD and blocks viral entry: Strategy to combat COVID-19.iScience. 2022 Mar 18;25(3):103856. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103856. Epub 2022 Feb 2. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35128350 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

