Epidemiological characteristics of the COVID-19 outbreak in a secondary hospital in Spain
- PMID: 32663494
- PMCID: PMC7834034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajic.2020.07.014
Epidemiological characteristics of the COVID-19 outbreak in a secondary hospital in Spain
Abstract
Objectives: In 2019 Chinese authorities alerted of the appearance of a cluster of cases of unknown pneumonia related to a new type of coronavirus. Spain is among the most affected countries. Our aim is to describe the cases of COVID-19 at Infanta Sofía University Hospital (Madrid), a public secondary hospital that increased its hospital beds to provide assistance during the outbreak.
Methods: Retrospective descriptive study of cases that met COVID-19 clinical diagnosis criteria or had a positive PCR test from February 27 to June 29, 2020. A description of demographic variables, hospital stay, mortality and the epidemiological curve was performed.
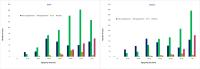
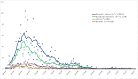
Results: Of 1,828 confirmed cases, 64.4% were hospitalised, 5.6% were admitted to the ICU. About 52.2% were male. The median age was 63.2 years. About 13.1% were nursing home residents. Nineteen percent were of Latin American origin of which 6.8% were admitted to the ICU. Overall case fatality was 14.6%. We observed a biphasic epidemiological curve.
Conclusions: Sixty to 79-year-old males were admitted and deceased more often than women. Mortality reached 14.7%. Latin Americans were admitted more often to the ICU. Further studies about epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 in hospitals are necessary.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; Epidemiology; Hospital; Infection control; Pandemics; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Spanish Ministry of Health. New coronavirus disease. https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/ccayes/alertasActual.... Accessed April 26, 2020.
-
- Reuters. Wuhan lockdown ‘unprecedented’, shows commitment to contain virus: WHO representative in China. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-health-who-idUSKBN1ZM1G9. Accessed April 26, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... Accessed April 26, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS): Status of the Outbreak and Lessons for the Immediate Future. 2003. SARS: a puzzling and difficult new disease.https://www.who.int/csr/media/sars_wha.pdf?ua=1 Available at: Accessed April 26, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

