Effect of thyrotropin suppressive therapy on heart rate variability and QT dispersion in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
- PMID: 32664162
- PMCID: PMC7360250
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021190
Effect of thyrotropin suppressive therapy on heart rate variability and QT dispersion in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Abstract
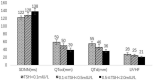
The effects of thyrotropin (TSH) suppressive therapy on autonomic regulation and ventricular repolarization in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) have not been elucidated. The aim of present study was to evaluate variation in heart rate variability (HRV) and QT dispersion after TSH suppressive therapy in patients with DTC.Cases, defined as 271 patients with DTC within 1 year of exogenous levothyroxine, and all patients underwent a full history, physical examination, including standard 12 lead electrocardiogram (ECG), and 24 h ambulatory ECG monitoring (Holter) with normal free thyroxine (FT4) and free triiodothyronine (FT3) with levothyroxine. To evaluate effects of TSH suppressive therapy on HRV and QT dispersion, patients were divided into three groups according to different levels of TSH: TSH < 0.1 mIU/L group and 0.1 ≤ TSH < 0.5 mIU/L group were as TSH suppression groups, and 0.5 ≤ TSH < 2.0 mIU/L group was as TSH replacement group.Comparing with 0.5 ≤ TSH < 2.0 mIU/L group, significant changes in both time and frequency domain of HRV and QT dispersion were observed in TSH < 0.1 mIU/L group (P < .001: SDNN, SDANN, HF, LF/HF, QTd, and QTcd; P < .05: rMSSD) and 0.1 ≤ TSH < 0.5 mIU/L group (P < .001: SDNN, HF, LF/HF, QTd, and QTcd), and especially were more pronounced in TSH < 0.1 mIU/L group. Moreover, we found that TSH level was proportional to SDNN (β = 15.829, P < .001), but inversely proportional to LF/HF (β = -0.671, P < .001), QTd (β = -16.674, P < .001) and QTcd (β = -18.314, P < .001) in DTC patients with exogenous levothyroxine.Compared with euthyroid state, patients with suppressed serum TSH have increased sympathetic activity in the presence of diminished vagal tone, ultimately showed sympathovagal imbalance and with an increased inhomogeneity of ventricular recovery times. These findings revealed that TSH suppression therapy had a significant impact on cardiovascular system and had certain guiding role in the treatment and management of patients with DTC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do Different TSH Suppression Levels Effect Heart Rate Variability and QT Dispersions in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer?Endocr Res. 2025 Feb;50(1):28-35. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2024.2383669. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Endocr Res. 2025. PMID: 39051971
-
Heart rate variability and QT dispersion in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism.Biomed Pharmacother. 2006 Sep;60(8):425-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2006.07.009. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16930934 Clinical Trial.
-
Sympatho-vagal control of heart rate variability in patients treated with suppressive doses of L-thyroxine for thyroid cancer.Eur J Endocrinol. 2005 Jun;152(6):819-24. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.01918. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15941920
-
Benefits of thyrotropin suppression versus the risks of adverse effects in differentiated thyroid cancer.Thyroid. 2010 Feb;20(2):135-46. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0311. Thyroid. 2010. PMID: 20151821 Review.
-
[Treatment with L-thyroxine for differentiated thyroid carcinoma].Wiad Lek. 2001;54 Suppl 1:368-72. Wiad Lek. 2001. PMID: 12182051 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Association between thyroid cancer and cardiovascular disease risk: a nationwide observation study.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 2;12(1):18438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22462-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36323730 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Cardiac Repolarization in Thyroid Diseases: Results of an Observational Study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 23;8:738517. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.738517. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34888359 Free PMC article.
-
Levothyroxine therapy in thyroidectomized patients: ongoing challenges and controversies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 26;16:1582734. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1582734. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40491597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levothyroxine Treatment and the Risk of Cardiac Arrhythmias - Focus on the Patient Submitted to Thyroid Surgery.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 4;12:758043. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.758043. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34803920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silent Signals: Analyzing Repolarization Heterogeneity and Autonomic Modulation in Children With Euthyroid Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.Cureus. 2025 Mar 20;17(3):e80925. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80925. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hovens GC, Stokkel MP, Kievit J, et al. Associations of serum thyrotropin concentrations with recurrence and death in differentiated thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:2610–5. - PubMed
-
- Beekman RE, van Hardeveld C, Simonides WS. Effect of thyroid state on cytosolic free calcium in resting and electrically stimulated cardiac myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1988;969:18–27. - PubMed
-
- Sunagawa M, Yamakawa M, Shimabukuro M, et al. Electrophysiologic characteristics of atrial myocytes in levo-thyroxine-treated rats. Thyroid 2005;15:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi Y, Cui G, Sen L. Acute effects of thyroid hormone on inward rectifier potassium channel currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Endocrinology 1996;137:4744–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

