Asymmetric Dinuclear Lanthanide(III) Complexes from the Use of a Ligand Derived from 2-Acetylpyridine and Picolinoylhydrazide: Synthetic, Structural and Magnetic Studies
- PMID: 32664199
- PMCID: PMC7397153
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25143153
Asymmetric Dinuclear Lanthanide(III) Complexes from the Use of a Ligand Derived from 2-Acetylpyridine and Picolinoylhydrazide: Synthetic, Structural and Magnetic Studies
Abstract
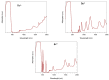
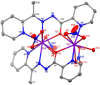
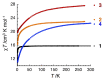
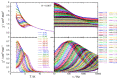
A family of four Ln(III) complexes has been synthesized with the general formula [Ln2(NO3)4(L)2(S)] (Ln = Gd, Tb, Er, and S = H2O; 1, 2 and 4, respectively/Ln = Dy, S = MeOH, complex 3), where HL is the flexible ditopic ligand N'-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2-carbohydrazide. The structures of isostructural MeOH/H2O solvates of these complexes were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The two LnIII ions are doubly bridged by the deprotonated oxygen atoms of two "head-to-head" 2.21011 (Harris notation) L¯ ligands, forming a central, nearly rhombic {LnIII2(μ-OR)2}4+ core. Two bidentate chelating nitrato groups complete a sphenocoronal 10-coordination at one metal ion, while two bidentate chelating nitrato groups and one solvent molecule (H2O or MeOH) complete a spherical capped square antiprismatic 9-coordination at the other. The structures are critically compared with those of other, previously reported metal complexes of HL or L¯. The IR spectra of 1-4 are discussed in terms of the coordination modes of the organic and inorganic ligands involved. The f-f transitions in the solid-state (diffuse reflectance) spectra of the Tb(III), Dy(III), and Er(III) complexes have been fully assigned in the UV/Vis and near-IR regions. Magnetic susceptibility studies in the 1.85-300 K range reveal the presence of weak, intramolecular GdIII∙∙∙GdIII antiferromagnetic exchange interactions in 1 [J/kB = -0.020(6) K based on the spin Hamiltonian Ĥ = -2J(ŜGd1∙ ŜGd2)] and probably weak antiferromagnetic LnIII∙∙∙LnIII exchange interactions in 2-4. Ac susceptibility measurements in zero dc field do not show frequency dependent out-of-phase signals, and this experimental fact is discussed for 3 in terms of the magnetic anisotropy axis for each DyIII center and the oblate electron density of this metal ion. Complexes 3 and 4 are Single-Molecule Magnets (SMMs) and this behavior is optimally observed under external dc fields of 600 and 1000 Oe, respectively. The magnetization relaxation pathways are discussed and a satisfactory fit of the temperature and field dependencies of the relaxation time τ was achieved considering a model that employs Raman, direct, and Orbach relaxation mechanisms.
Keywords: asymmetric dinuclear lanthanide(III) complexes; dysprosium(III) and erbium(III) single-molecule magnets; magnetic properties; magnetization relaxation pathways; metal complexes of N’-(1-(1-pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2-carbohydrazide; single-crystal X-ray structures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synthesis, structure, luminescent, and magnetic properties of carbonato-bridged Zn(II)2Ln(III)2 complexes [(μ4-CO3)2{Zn(II)L(n)Ln(III)(NO3)}2] (Ln(III) = Gd(III), Tb(III), Dy(III); L(1) = N,N'-bis(3-methoxy-2-oxybenzylidene)-1,3-propanediaminato, L(2) = N,N'-bis(3-ethoxy-2-oxybenzylidene)-1,3-propanediaminato).Inorg Chem. 2013 Nov 4;52(21):12828-41. doi: 10.1021/ic4022273. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 24151881
-
Syntheses, structures, and magnetic properties of acetato- and diphenolato-bridged 3d-4f binuclear complexes [M(3-MeOsaltn)(MeOH)x(ac)Ln(hfac)2] (M = Zn(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II); Ln = La(III), Gd(III), Tb(III), Dy(III); 3-MeOsaltn = N,N'-bis(3-methoxy-2-oxybenzylidene)-1,3-propanediaminato; ac = acetato; hfac = hexafluoroacetylacetonato; x = 0 or 1).Inorg Chem. 2013 May 20;52(10):6160-78. doi: 10.1021/ic400594u. Epub 2013 May 6. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23646986
-
Carbonato-bridged Ni(II)2Ln(III)2 (Ln(III) = Gd(III), Tb(III), Dy(III)) complexes generated by atmospheric CO2 fixation and their single-molecule-magnet behavior: [(μ4-CO3)2{Ni(II)(3-MeOsaltn)(MeOH or H2O)Ln(III)(NO3)}2]·solvent [3-MeOsaltn = N,N'-bis(3-methoxy-2-oxybenzylidene)-1,3-propanediaminato].Inorg Chem. 2013 Jun 17;52(12):7218-29. doi: 10.1021/ic4008312. Epub 2013 May 24. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23706096
-
Isotopic enrichment in lanthanide coordination complexes: contribution to single-molecule magnets and spin qudit insights.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Jul 6;59(55):8520-8531. doi: 10.1039/d3cc01722b. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37335142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mononuclear Dysprosium Alkoxide and Aryloxide Single-Molecule Magnets.Chemistry. 2021 May 17;27(28):7625-7645. doi: 10.1002/chem.202100085. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 33555090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dinuclear Lanthanide(III) Complexes from the Use of Methyl 2-Pyridyl Ketoxime: Synthetic, Structural, and Physical Studies.Molecules. 2021 Mar 15;26(6):1622. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061622. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33804026 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Lanthanide(III) Porphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks: Structure, Gas Adsorption, and Magnetic Properties.ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 17;6(38):24637-24649. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03327. eCollection 2021 Sep 28. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34604646 Free PMC article.
-
A trivalent 4f complex with two bis-silylamide ligands displaying slow magnetic relaxation.Nat Chem. 2023 Aug;15(8):1100-1107. doi: 10.1038/s41557-023-01208-y. Epub 2023 May 25. Nat Chem. 2023. PMID: 37231297
-
Exchange Bias in a Dinuclear Erbium Single-Molecule Magnet Bridged by a Helicene Ligand.Inorg Chem. 2025 Jul 28;64(29):15088-15097. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5c01992. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Inorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 40673895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cador O., Le Guennic B., Pointillart F. Electro-activity and magnetic switching in lanthanide-based single-molecule magnets. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019;6:3398–3417. doi: 10.1039/C9QI00875F. - DOI
-
- Gatteschi D., Sessoli R., Villain J. Molecular Nanomagnets. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2006.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

