Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Cancer Patients with Mild to Severe Liver Dysfunction: Adjunctive Role of the ALBI Grade
- PMID: 32664319
- PMCID: PMC7408648
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12071862
Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Cancer Patients with Mild to Severe Liver Dysfunction: Adjunctive Role of the ALBI Grade
Abstract
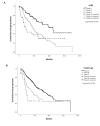
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have shown positive results in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As liver function contributes to prognosis, its precise assessment is necessary for the safe prescribing and clinical development of ICI in HCC. We tested the accuracy of the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade as an alternative prognostic biomarker to the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP). In a prospectively maintained multi-centre dataset of HCC patients, we assessed safety and efficacy of ICI across varying levels of liver dysfunction described by CTP (A to C) and ALBI grade and evaluated uni- and multi-variable predictors of overall (OS) and post-immunotherapy survival (PIOS). We studied 341 patients treated with programmed-death pathway inhibitors (n = 290, 85%). Pre-treatment ALBI independently predicted for OS, with median OS of 22.5, 9.6, and 4.6 months across grades (p < 0.001). ALBI was superior to CTP in predicting 90-days mortality with area under the curve values of 0.65 (95% CI 0.57-0.74) versus 0.63 (95% CI 0.54-0.72). ALBI grade at ICI cessation independently predicted for PIOS (p < 0.001). Following adjustment for ICI regimen, neither ALBI nor CTP predicted for overall response rates or treatment-emerging adverse events (p > 0.05). ALBI grade identifies a subset of patients with prolonged survival prior to and after ICI therapy, lending itself as an optimal stratifying biomarker to optimise sequencing of systemic therapies in advanced HCC.
Keywords: bilirubin; biomarkers; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
D.J.P. received lecture fees from ViiV Healthcare, Bayer Healthcare and travel expenses from BMS and Bayer Healthcare; consulting fees for Mina Therapeutics, EISAI, Roche, Astra Zeneca; received research funding (to institution) from MSD, BMS. D.B. has received lecture and speaker fees from Bayer Healthcare and the Falk Foundation Germany. L.R. received lectures fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Eisai, Gilead, Ipsen, Lilly, Roche, Sanofi; advisory board/consulting fees from Amgen, ArQule, AstraZeneca, Basilea, Bayer, Celgene, Eisai, Exelixis, Hengrui, Incyte, Ipsen, Lilly, MSD, Nerviano Medical Sciences, Roche, Sanofi; travel expenses from Ipsen; received research funding (to institution) from Agios, ARMO BioSciences, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Eisai, Exelixis, Incyte, Ipsen, Lilly, MSD. N.P. received lecture fees from AbbVie and Gilead; travel expenses from ArQule. Y.-H.H has received advisory board/consulting fees for BMS, MSD, Bayer Healthcare, IPSEN, EISAI, Gilead and Lilly. A.S. received research funding (to institution) from AstraZeneca, Exelixis, BMS and Clovis; advisory board/consulting fees from BMS, AstraZeneca, and Exelixis. There are no other personal or financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Albumin - bilirubin (ALBI) versus Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) in prognosis of HCC after stereotactic body radiation therapy.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Mar 27;14(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1251-y. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30917853 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing various scoring system for predicting overall survival according to treatment modalities in hepatocellular carcinoma focused on Platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) and albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade: A nationwide cohort study.PLoS One. 2019 May 2;14(5):e0216173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216173. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31048923 Free PMC article.
-
ALBI and PALBI grade predict survival for HCC across treatment modalities and BCLC stages in the MELD Era.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Apr;32(4):879-886. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13608. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27696519
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and albumin bilirubin grade in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Sep 7;26(33):5022-5049. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.5022. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32952347 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the Albumin-Bilirubin Grade in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transplant Proc. 2019 Dec;51(10):3338-3346. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.08.027. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Transplant Proc. 2019. PMID: 31732203
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of pre-treatment ALBI grade in advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint therapy.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 23;11(1):15057. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94336-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34301991 Free PMC article.
-
The Performance of a Survival Nomogram and Albumin-Bilirubin Grade as Prognostic Tools in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with FOLFOX4.J Pers Med. 2024 Apr 11;14(4):403. doi: 10.3390/jpm14040403. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38673030 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Response in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7640. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087640. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical usefulness of newly developed prognostic predictive score for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Apr;7(4):e2042. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2042. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38577725 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of itacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in advanced hepatocellular cancer: Phase 1b trial (JAKAL).Future Oncol. 2024;20(36):2839-2847. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2396795. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39283290 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

