Vasodilatory Effect of Phellinus linteus Extract in Rat Mesenteric Arteries
- PMID: 32664327
- PMCID: PMC7397296
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25143160
Vasodilatory Effect of Phellinus linteus Extract in Rat Mesenteric Arteries
Abstract
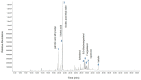
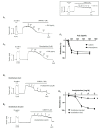
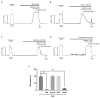
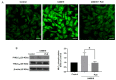
Phellinus linteus is a well-known medicinal mushroom that is widely used in Asian countries. In several experimental models, Phellinus linteus extracts were reported to have various biological effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, hepatoprotective, anti-diabetic, neuroprotective, and anti-angiogenic activity. In the present study, several bioactive compounds, including palmitic acid ethyl ester and linoleic acid, were identified in Phellinus linteus. The intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (IKCa) plays an important role in the regulation of the vascular smooth muscle cells' (VSMCs) contraction and relaxation. The activation of the IKCa channel causes the hyperpolarization and relaxation of VSMCs. To examine whether Phellinus linteus extract causes vasodilation in the mesenteric arteries of rats, we measured the isometric tension using a wire myograph. After the arteries were pre-contracted with U46619 (a thromboxane analogue, 1 µM), Phellinus linteus extract was administered. The Phellinus linteus extract induced vasodilation in a dose-dependent manner, which was independent of the endothelium. To further investigate the mechanism, we used the non-selective K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA). TEA significantly abolished Phellinus linteus extract-induced vasodilation. Thus, we tested three different types of K+ channel blockers: iberiotoxin (BKca channel blocker), apamin (SKca channel blocker), and charybdotoxin (IKca channel blocker). Charybdotoxin significantly inhibited Phellinus linteus extract-induced relaxation, while there was no effect from apamin and iberiotoxin. Membrane potential was measured using the voltage-sensitive dye bis-(1,3-dibutylbarbituric acid)-trimethine oxonol (DiBAC4(3)) in the primary isolated vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). We found that the Phellinus linteus extract induced hyperpolarization of VSMCs, which is associated with a reduced phosphorylation level of 20 KDa myosin light chain (MLC20).
Keywords: Kca channels; Phellinus linteus; mesenteric artery; relaxation; vasodilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparison of EDHF-mediated and anandamide-induced relaxations in the rat isolated mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Dec;122(8):1573-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701546. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9422801 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 diabetes: increased expression and contribution of IKCa channels to vasodilation in small mesenteric arteries of ZDF rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):H1093-102. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00240.2013. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25128173
-
Isoliquiritigenin-induced vasodilation by activating large-conductance Ca2+ -activated K+ channels in mouse mesenteric arteries.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019 Nov;46(11):1044-1052. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13156. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31394004
-
Phellinus linteus polysaccharides: A review on their preparation, structure-activity relationships, and drug delivery systems.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;258(Pt 1):128702. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128702. Epub 2023 Dec 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38072341 Review.
-
Recent advances in the bioactive polysaccharides and other key components from Phellinus spp. and their pharmacological effects: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Dec 1;222(Pt B):3108-3128. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.085. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 36243155 Review.
Cited by
-
Compounds purified from edible fungi fight against chronic inflammation through oxidative stress regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 9;13:974794. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.974794. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wild Mushrooms: A Hidden Treasure of Novel Bioactive Compounds.Int J Anal Chem. 2023 Sep 22;2023:6694961. doi: 10.1155/2023/6694961. eCollection 2023. Int J Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37781342 Free PMC article.
-
Vasodilatory Effect of Alpinia officinarum Extract in Rat Mesenteric Arteries.Molecules. 2022 Apr 22;27(9):2711. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092711. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566064 Free PMC article.
-
Vasorelaxant Effect of Trachelospermi caulis Extract on Rat Mesenteric Resistance Arteries.Molecules. 2022 Aug 19;27(16):5300. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165300. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014534 Free PMC article.
-
Deuterohemin-Ala-His-Thr-Val-Glu-Lys (DhHP-6) Mimicking Enzyme as Synergistic Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Material for Periodontitis Therapy.Biomimetics (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;7(4):240. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics7040240. Biomimetics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36546940 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

