The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways
- PMID: 32664401
- PMCID: PMC7412373
- DOI: 10.3390/v12070746
The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways
Abstract
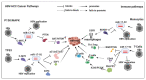
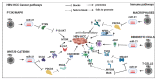
Currently, the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [HBV-HCC] relies on blunt tools that are unable to offer effective therapy for later stage pathogenesis. The potential of miRNA to treat HBV-HCC offer a more targeted approach to managing this lethal carcinoma; however, the complexity of miRNA as an ancillary regulator of the immune system remains poorly understood. This review examines the overlapping roles of HBx-dysregulated miRNA in HBV-HCC and immune pathways and seeks to demonstrate that specific miRNA response in immune cells is not independent of their expression in hepatocytes. This interplay between the two pathways may provide us with the possibility of using candidate miRNA to manipulate this interaction as a potential therapeutic option.
Keywords: HBx protein; dysregulated; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Epigenetic Modulation of Cancer and Immune Pathways in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Influence of HBx and miRNA Dysregulation.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:661204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661204. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA-210-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G401-G409. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00269.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31905024
-
miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 14;22(22):5183-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27298561 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of B7-H4 and hepatitis B virus X in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 14;22(18):4538-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4538. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27182163 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic Viruses as Entropic Drivers of Cancer Evolution.Front Virol. 2021 Nov;1:753366. doi: 10.3389/fviro.2021.753366. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Front Virol. 2021. PMID: 35141704 Free PMC article.
-
The social and occupational consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic among patients with multiple sclerosis in three distinct populations: A web-based cross-sectional survey.Neurol Perspect. 2022 Jan-Mar;2(1):9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neurop.2021.10.004. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Neurol Perspect. 2022. PMID: 38620860 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, Pathological and Genetic Characteristics of Pediatric Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Hepatitis B Virus Infection.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021 May 10;8:361-367. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S306963. eCollection 2021. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021. PMID: 34007834 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of microRNAs in virus-mediated inflammation.J Inflamm (Lond). 2024 Nov 4;21(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12950-024-00417-7. J Inflamm (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39497125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compartmentalisation of Hepatitis B virus X gene evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment and the genotype-phenotype correlation of tumorigenicity in HBV-related patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):2486-2501. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2125344. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 36102940 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

