SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses Do Not Predict COVID-19 Disease Severity
- PMID: 32666092
- PMCID: PMC7454292
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa123
SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses Do Not Predict COVID-19 Disease Severity
Abstract
Objectives: Initial reports indicate adequate performance of some serology-based severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) assays. However, additional studies are required to facilitate interpretation of results, including how antibody levels impact immunity and disease course.
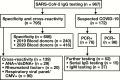
Methods: A total of 967 subjects were tested for IgG antibodies reactive to SARS-CoV-2, including 172 suspected cases of SARS-CoV-2, 656 plasma samples from healthy donors, 49 sera from patients with rheumatic disease, and 90 specimens from individuals positive for polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based respiratory viral panel. A subgroup of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive cases was tested for IgM antibodies by proteome array method.
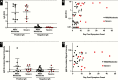
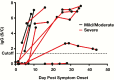
Results: All specificity and cross-reactivity specimens were negative for SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies (0/795, 0%). Positive agreement of IgG with PCR was 83% of samples confirmed to be more than 14 days from symptom onset, with less than 100% sensitivity attributable to a case with severe immunosuppression. Virus-specific IgM was positive in a higher proportion of cases less than 3 days from symptom onset. No association was observed between mild and severe disease course with respect to IgG and IgM levels.
Conclusions: The studied SARS-CoV-2 IgG assay had 100% specificity and no adverse cross-reactivity. Measures of IgG and IgM antibodies did not predict disease severity in our patient population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Global health; Immunology; Microbiology; SARS-CoV-2.
© American Society for Clinical Pathology, 2020.
Figures

Comment in
-
Individuals With Less Severe Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection May Not Develop Long-Lasting Humoral Immunity.Am J Clin Pathol. 2021 Feb 4;155(2):320. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa233. Am J Clin Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33219817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) real-time RT-PCR diagnostic panel for emergency use only: instructions for use https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download. Accessed June 12, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Laboratory testing for 2019-nCoV in humans https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica.... Accessed March 31, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

