Applying high-throughput sequencing to identify and evaluate foetal chromosomal deletion and duplication
- PMID: 32667743
- PMCID: PMC7520324
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15593
Applying high-throughput sequencing to identify and evaluate foetal chromosomal deletion and duplication
Abstract
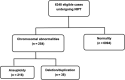
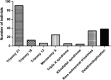
The present study aimed to estimate the clinical performance of non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) based on high-throughput sequencing method for the detection of foetal chromosomal deletions and duplications. A total of 6348 pregnant women receiving NIPT using high-throughput sequencing method were included in our study. They all conceived naturally, without twins, triplets or multiple births. Individuals showing abnormalities in NIPT received invasive ultrasound-guided amniocentesis for chromosomal karyotype and microarray analysis at 18-24 weeks of pregnancy. Detection results of foetal chromosomal deletions and duplications were compared between high-throughput sequencing method and chromosomal karyotype and microarray analysis. Thirty-eight individuals were identified to show 51 chromosomal deletions/duplications via high-throughput sequencing method. In subsequent chromosomal karyotype and microarray analysis, 34 subchromosomal deletions/duplications were identified in 26 pregnant women. The observed deletions and duplications ranged from 1.05 to 17.98 Mb. Detection accuracy for these deletions and duplications was 66.7%. Twenty-one deletions and duplications were found to be correlated with the known abnormalities. NIPT based on high-throughput sequencing technique is able to identify foetal chromosomal deletions and duplications, but its sensitivity and specificity were not explored. Further progress should be made to reduce false-positive results.
Keywords: cell-free foetal DNA; chromosomal abnormalities; chromosomal deletions/duplications; high-throughput sequencing; non-invasive prenatal testing.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

