CORR Synthesis: When Should We Be Skeptical of Clinical Prediction Models?
- PMID: 32667756
- PMCID: PMC7899395
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001367
CORR Synthesis: When Should We Be Skeptical of Clinical Prediction Models?
Conflict of interest statement
Each author certifies that neither he, nor any members of his immediate family, have any commercial associations (such as consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures
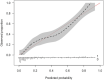
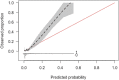
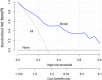


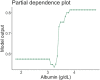
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: CORR Synthesis: When Should We Be Skeptical of Clinical Prediction Models?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022 Nov 1;480(11):2271-2273. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002395. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022. PMID: 36083689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alba AC, Agoritsas T, Walsh M, Hanna S, Iorio A, Devereaux P, McGinn T, Guyatt G. Discrimination and calibration of clinical prediction models: users’ guides to the medical literature. JAMA. 2017;318:1377-1384. - PubMed
-
- Ambler G, Omar RZ, Royston P. A comparison of imputation techniques for handling missing predictor values in a risk model with a binary outcome. Stat Methods Med Res. 2007;16:277-298. - PubMed
-
- Bellazzi R, Zupan B. Predictive data mining in clinical medicine: current issues and guidelines. Int J Med Inform. 2008;77:81-97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

