Mitochondrial Metabolism as a Target for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 32668195
- PMCID: PMC7483781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.019
Mitochondrial Metabolism as a Target for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
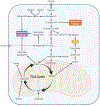
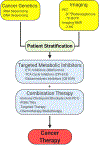
Recent evidence in humans and mice supports the notion that mitochondrial metabolism is active and necessary for tumor growth. Mitochondrial metabolism supports tumor anabolism by providing key metabolites for macromolecule synthesis and generating oncometabolites to maintain the cancer phenotype. Moreover, there are multiple clinical trials testing the efficacy of inhibiting mitochondrial metabolism as a new cancer therapeutic treatment. In this review, we discuss the rationale of using these anti-cancer agents in clinical trials and highlight how to effectively utilize them in different tumor contexts.
Keywords: metformin; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests N.S.C. is an SAB member of Raphael Pharmaceuticals (Devimistat – CPI-613).
Figures
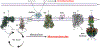


References
-
- Algire C, Amrein L, Bazile M, David S, Zakikhani M, and Pollak M (2011). Diet and tumor LKB1 expression interact to determine sensitivity to anti-neoplastic effects of metformin in vivo. Oncogene 30, 1174–1182. - PubMed
-
- Alistar AT, Desnoyers R, D’Agostino RJ, and Pasche B (2016). CPI-613 enhances FOLFIRINoX response rate in stage IV pancreatic cancer. Ann. Oncol. 27, VI228.
-
- Arrieta O, Barrón F, Padilla MS, Avilés-Salas A, Ramírez-Tirado LA, Arguelles Jiménez MJ, Vergara E, Zatarain-Barrón ZL, Hernández-Pedro N, Cardona AF, et al. (2019). Effect of metformin plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors compared with tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated lung adenocarcinoma: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 5, e192553. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

