Human-IgG-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Block the SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 32668215
- PMCID: PMC7332464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107918
Human-IgG-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Block the SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
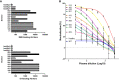
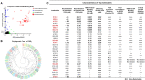
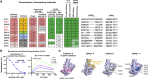
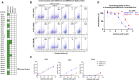
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a worldwide threat to humans, and neutralizing antibodies have therapeutic potential. We have purified more than 1,000 memory B cells specific to SARS-CoV-2 S1 or its RBD (receptor binding domain) and obtain 729 paired heavy- and light-chain fragments. Among these, 178 antibodies test positive for antigen binding, and the majority of the top 17 binders with EC50 below 1 nM are RBD binders. Furthermore, we identify 11 neutralizing antibodies, eight of which show IC50 within 10 nM, and the best one, 414-1, with IC50 of 1.75 nM. Through epitope mapping, we find three main epitopes in RBD recognized by these antibodies, and epitope-B antibody 553-15 could substantially enhance the neutralizing abilities of most of the other antibodies. We also find that 515-5 could cross neutralize the SARS-CoV pseudovirus. Altogether, our study provides 11 potent human neutralizing antibodies for COVID-19 as therapeutic candidates.
Keywords: COVID-19; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; cross-neutralizing antibody; epitope; human antibodies; infection; neutralizing antibodies; spike protein.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests Fei Lan is a shareholder and a scientific advisor of Active Motif China. Yanan Lu, Fei Lan, Jianqing Xu, Longfei Ding, Jinkai Wan, Shenghui Xing, and Yongheng Wang are listed as inventors on a patent application related to this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike.Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7821):450-456. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2571-7. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32698192
-
A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.Science. 2020 Aug 7;369(6504):650-655. doi: 10.1126/science.abc6952. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Science. 2020. PMID: 32571838 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a SARS-CoV-2-Infected Individual Reveals Development of Potent Neutralizing Antibodies with Limited Somatic Mutation.Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):98-105.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32561270 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SARS-CoV2 Spike Protein Receptor Binding Domain by Therapeutic Antibodies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110559. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110559. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32768882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor-binding domain-specific human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Sep 22;5(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00318-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32963228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-based Design of a Specific, Homogeneous Luminescence Enzyme Reporter Assay for SARS-CoV-2.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jun 25;433(13):166983. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166983. Epub 2021 Apr 8. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33839165 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and modulation of syncytia.Cell. 2021 Jun 10;184(12):3192-3204.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.033. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33974910 Free PMC article.
-
The instantly blocking-based fluorescent immunochromatographic assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Sep 5;13:1203625. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1203625. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37736103 Free PMC article.
-
Tetravalent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Show Enhanced Potency and Resistance to Escape Mutations.J Mol Biol. 2021 Sep 17;433(19):167177. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167177. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34329642 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Sensitive Inhibitor Screening Using Magnetically Modulated Biosensors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 14;21(14):4814. doi: 10.3390/s21144814. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Callaway E., Cyranoski D., Mallapaty S., Stoye E., Tollefson J. The coronavirus pandemic in five powerful charts. Nature. 2020;579:482–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

