Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice
- PMID: 32668216
- PMCID: PMC7340027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940
Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice
Abstract
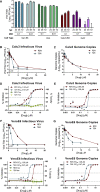
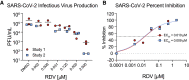
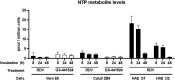
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of the novel viral disease COVID-19. With no approved therapies, this pandemic illustrates the urgent need for broad-spectrum antiviral countermeasures against SARS-CoV-2 and future emerging CoVs. We report that remdesivir (RDV) potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in human lung cells and primary human airway epithelial cultures (EC50 = 0.01 μM). Weaker activity is observed in Vero E6 cells (EC50 = 1.65 μM) because of their low capacity to metabolize RDV. To rapidly evaluate in vivo efficacy, we engineered a chimeric SARS-CoV encoding the viral target of RDV, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2. In mice infected with the chimeric virus, therapeutic RDV administration diminishes lung viral load and improves pulmonary function compared with vehicle-treated animals. These data demonstrate that RDV is potently active against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and in vivo, supporting its further clinical testing for treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; GS-441524; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RdRp; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; coronavirus; mouse; remdesivir; therapeutic.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors affiliated with Gilead Sciences, Inc. are employees of the company and may own company stock.
Figures


Update of
-
Remdesivir potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 27:2020.04.27.064279. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.27.064279. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep. 2020 Jul 21;32(3):107940. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940. PMID: 32511392 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Agostini M.L., Pruijssers A.J., Chappell J.D., Gribble J., Lu X., Andres E.L., Bluemling G.R., Lockwood M.A., Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C. Small-Molecule Antiviral β-d-N4-Hydroxycytidine Inhibits a Proofreading-Intact Coronavirus with a High Genetic Barrier to Resistance. J. Virol. 2019;93:e01348-19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Appleby T.C., Perry J.K., Murakami E., Barauskas O., Feng J., Cho A., Fox D., 3rd, Wetmore D.R., McGrath M.E., Ray A.S. Viral replication. Structural basis for RNA replication by the hepatitis C virus polymerase. Science. 2015;347:771–775. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

