The Cdc48 Complex Alleviates the Cytotoxicity of Misfolded Proteins by Regulating Ubiquitin Homeostasis
- PMID: 32668237
- PMCID: PMC7392062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107898
The Cdc48 Complex Alleviates the Cytotoxicity of Misfolded Proteins by Regulating Ubiquitin Homeostasis
Abstract
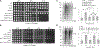
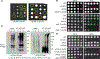
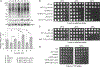
The accumulation of misfolded proteins is associated with multiple neurodegenerative disorders, but it remains poorly defined how this accumulation causes cytotoxicity. Here, we demonstrate that the Cdc48/p97 segregase machinery drives the clearance of ubiquitinated model misfolded protein Huntingtin (Htt103QP) and limits its aggregation. Nuclear ubiquitin ligase San1 acts upstream of Cdc48 to ubiquitinate Htt103QP. Unexpectedly, deletion of SAN1 and/or its cytosolic counterpart UBR1 rescues the toxicity associated with Cdc48 deficiency, suggesting that ubiquitin depletion, rather than compromised proteolysis of misfolded proteins, causes the growth defect in cells with Cdc48 deficiency. Indeed, Cdc48 deficiency leads to elevated protein ubiquitination levels and decreased free ubiquitin, which depends on San1/Ubr1. Furthermore, enhancing free ubiquitin levels rescues the toxicity in various Cdc48 pathway mutants and restores normal turnover of a known Cdc48-independent substrate. Our work highlights a previously unappreciated function for Cdc48 in ensuring the regeneration of monoubiquitin that is critical for normal cellular function.
Keywords: Cdc48; San1/Ubr1 E3 ligases; mutated Huntingtin; proteotoxicity; ubiquitin homeostasis.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests There are no competing interests.
Figures
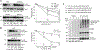


References
-
- Aguado A, Fernández-Higuero JA, Moro F, and Muga A (2015). Chaperone-assisted protein aggregate reactivation: Different solutions for the same problem. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 580, 121–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

