Switching to Bictegravir, Emtricitabine, and Tenofovir Alafenamide in Virologically Suppressed Adults With Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- PMID: 32668455
- PMCID: PMC8282313
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa988
Switching to Bictegravir, Emtricitabine, and Tenofovir Alafenamide in Virologically Suppressed Adults With Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Abstract
Background: Bictegravir (B)/emtricitabine (F)/tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) is guideline-recommended treatment for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). We evaluated whether people receiving dolutegravir (DTG) plus F/TAF or F/TDF (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) with viral suppression can switch to B/F/TAF without compromising safety or efficacy, regardless of preexisting nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) resistance.
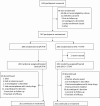
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, active-controlled, noninferiority trial, we enrolled adults who were virologically suppressed for ≥6 months before screening (with documented/suspected NRTI resistance) or ≥3 months before screening (with no documented/suspected NRTI resistance) on DTG plus either F/TDF or F/TAF. We randomly assigned (1:1) participants to switch to B/F/TAF or DTG + F/TAF once daily for 48 weeks, each with matching placebo. The primary endpoint was proportion of participants with plasma HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL at week 48 (snapshot algorithm); the prespecified noninferiority margin was 4%.
Results: Five hundred sixty-seven adults were randomized; 565 were treated (284 B/F/TAF, 281 DTG + F/TAF). At week 48, B/F/TAF was noninferior to DTG + F/TAF, as 0.4% (1/284) vs 1.1% (3/281) had HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL (difference, -0.7% [95.001% confidence interval {CI}, -2.8% to 1.0%]). There were no significant differences in efficacy among participants with suspected or confirmed prior NRTI resistance (n = 138). No participant had treatment-emergent drug resistance. Median weight change from baseline at week 48 was +1.3 kg (B/F/TAF) vs +1.1 kg (DTG + F/TAF) (P = .46). Weight change differed by baseline NRTIs (+2.2 kg [F/TDF] and +0.6 kg [F/TAF], P < .001), with no differences between B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TAF.
Conclusions: The single-tablet regimen B/F/TAF is a safe, effective option for people virologically suppressed on DTG plus either F/TDF or F/TAF, including in individuals with preexisting resistance to NRTIs.
Clinical trials registration: NCT03110380.
Keywords: HIV; INSTI; bictegravir; dolutegravir; tenofovir alafenamide.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- European AIDS Clinical Society. Guidelines, version 9.1, October 2018. Available at: http://www.eacsociety.org/files/2018_guidelines-9.1-english.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2020.
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents living with HIV.2019. Available at: http://www.aidsinfo.nih.gov/ContentFiles/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2020.
-
- Walmsley SL, Antela A, Clumeck N, et al. . SINGLE Investigators . Dolutegravir plus abacavir-lamivudine for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:1807–18. - PubMed
-
- Raffi F, Jaeger H, Quiros-Roldan E, et al. . extended SPRING-2 Study Group . Once-daily dolutegravir versus twice-daily raltegravir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (SPRING-2 study): 96 week results from a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2013; 13:927–35. - PubMed

