Discovery of M Protease Inhibitors Encoded by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32669265
- PMCID: PMC7449189
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00872-20
Discovery of M Protease Inhibitors Encoded by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
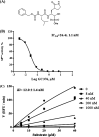
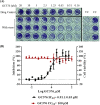
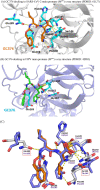
The coronavirus (CoV) disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome CoV-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a health threat worldwide. Viral main protease (Mpro, also called 3C-like protease [3CLpro]) is a therapeutic target for drug discovery. Herein, we report that GC376, a broad-spectrum inhibitor targeting Mpro in the picornavirus-like supercluster, is a potent inhibitor for the Mpro encoded by SARS-CoV-2, with a half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 26.4 ± 1.1 nM. In this study, we also show that GC376 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication with a half-maximum effective concentration (EC50) of 0.91 ± 0.03 μM. Only a small portion of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro was covalently modified in the excess of GC376 as evaluated by mass spectrometry analysis, indicating that improved inhibitors are needed. Subsequently, molecular docking analysis revealed that the recognition and binding groups of GC376 within the active site of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro provide important new information for the optimization of GC376. Given that sufficient safety and efficacy data are available for GC376 as an investigational veterinary drug, expedited development of GC376, or its optimized analogues, for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human is recommended.
Keywords: COVID-19; GC376; M protease; Mpro; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral research.
Copyright © 2020 Hung et al.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL. 2020. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579:270–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Muller MA, Niemeyer D, Jones TC, Vollmar P, Rothe C, Hoelscher M, Bleicker T, Brunink S, Schneider J, Ehmann R, Zwirglmaier K, Drosten C, Wendtner C. 2020. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 581:465–469. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

