Regulation of stem cell function and neuronal differentiation by HERV-K via mTOR pathway
- PMID: 32669437
- PMCID: PMC7395438
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2002427117
Regulation of stem cell function and neuronal differentiation by HERV-K via mTOR pathway
Abstract
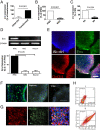
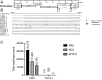
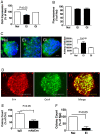
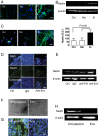
Stem cells are capable of unlimited proliferation but can be induced to form brain cells. Factors that specifically regulate human development are poorly understood. We found that human stem cells expressed high levels of the envelope protein of an endogenized human-specific retrovirus (HERV-K, HML-2) from loci in chromosomes 12 and 19. The envelope protein was expressed on the cell membrane of the stem cells and was critical in maintaining the stemness via interactions with CD98HC, leading to triggering of human-specific signaling pathways involving mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase (LPCAT1)-mediated epigenetic changes. Down-regulation or epigenetic silencing of HML-2 env resulted in dissociation of the stem cell colonies and enhanced differentiation along neuronal pathways. Thus HML-2 regulation is critical for human embryonic and neurodevelopment, while it's dysregulation may play a role in tumorigenesis and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: embryogenesis; endogenous retrovirus; neurogenesis; progenitor cells; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
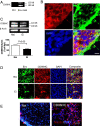
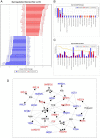
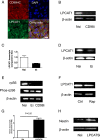

References
-
- Lander E. S. et al. .; International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium , Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Mi S., et al. , Syncytin is a captive retroviral envelope protein involved in human placental morphogenesis. Nature 403, 785–789 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Dupressoir A., Lavialle C., Heidmann T., From ancestral infectious retroviruses to bona fide cellular genes: Role of the captured syncytins in placentation. Placenta 33, 663–671 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

