Co-option of Plasmodium falciparum PP1 for egress from host erythrocytes
- PMID: 32669539
- PMCID: PMC7363832
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17306-1
Co-option of Plasmodium falciparum PP1 for egress from host erythrocytes
Abstract
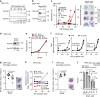
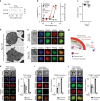
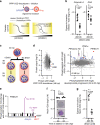
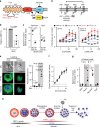
Asexual proliferation of the Plasmodium parasites that cause malaria follows a developmental program that alternates non-canonical intraerythrocytic replication with dissemination to new host cells. We carried out a functional analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum homolog of Protein Phosphatase 1 (PfPP1), a universally conserved cell cycle factor in eukaryotes, to investigate regulation of parasite proliferation. PfPP1 is indeed required for efficient replication, but is absolutely essential for egress of parasites from host red blood cells. By phosphoproteomic and chemical-genetic analysis, we isolate two functional targets of PfPP1 for egress: a HECT E3 protein-ubiquitin ligase; and GCα, a fusion protein composed of a guanylyl cyclase and a phospholipid transporter domain. We hypothesize that PfPP1 regulates lipid sensing by GCα and find that phosphatidylcholine stimulates PfPP1-dependent egress. PfPP1 acts as a key regulator that integrates multiple cell-intrinsic pathways with external signals to direct parasite egress from host cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Arnot DE, Ronander E, Bengtsson DC. The progression of the intra-erythrocytic cell cycle of Plasmodium falciparum and the role of the centriolar plaques in asynchronous mitotic division during schizogony. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011;41:71–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

