The Essential Thioredoxin Reductase of the Human Pathogenic Mold Aspergillus fumigatus Is a Promising Antifungal Target
- PMID: 32670238
- PMCID: PMC7330004
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01383
The Essential Thioredoxin Reductase of the Human Pathogenic Mold Aspergillus fumigatus Is a Promising Antifungal Target
Abstract
The identification of cellular targets for antifungal compounds is a cornerstone for the development of novel antimycotics, for which a significant need exists due to increasing numbers of susceptible patients, emerging pathogens, and evolving resistance. For the human pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus, the causative agent of the opportunistic disease aspergillosis, only a limited number of established targets and corresponding drugs are available. Among several targets that were postulated from a variety of experimental approaches, the conserved thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) activity encoded by the trxR gene was assessed in this study. Its essentiality could be confirmed following a conditional TetOFF promoter replacement strategy. Relevance of the trxR gene product for oxidative stress resistance was revealed and, most importantly, its requirement for full virulence of A. fumigatus in two different models of infection resembling invasive aspergillosis. Our findings complement the idea of targeting the reductase component of the fungal thioredoxin system for antifungal therapy.
Keywords: TetOFF; aspergillosis; conditional promoter replacement; essentiality; thioredoxin.
Copyright © 2020 Binder, Shadkchan, Osherov and Krappmann.
Figures
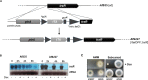
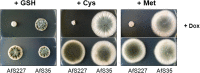
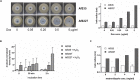
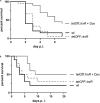
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

