Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Nonischemic Cardiomyopathies
- PMID: 32670469
- PMCID: PMC7350809
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-16-2-97
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Nonischemic Cardiomyopathies
Abstract
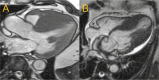
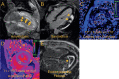
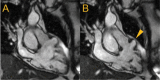
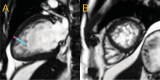
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) has emerged as a key modality to assess nonischemic cardiomyopathies. Its ability to detect cardiac morphology and function with fast cine imaging, myocardial edema with T2-based techniques, and fibrosis with late gadolinium enhancement techniques has enabled noninvasive characterization of cardiac tissue, thus helping clinicians assess cardiovascular risk and determine the most effective management strategy. Active investigations into parametric imaging techniques will further expand the potential clinical applications of CMR for cardiac tissue characterization. This review discusses the use of CMR techniques in characterizing the major morphofunctional phenotypes of nonischemic cardiomyopathies.
Keywords: cardiovascular magnetic resonance; nonischemic cardiomyopathies; parametric mapping; tissue characterization.
© 2020 Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas.
Figures


References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013 Oct 15;128(16):e240–327. - PubMed
-
- Arbustini E, Narula N, Tavazzi L et al. The MOGE(S) classification of cardiomyopathy for clinicians. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jul 22;64(3):304–18. - PubMed
-
- Schuster A, Morton G, Chiribiri A, Perera D, Vanoverschelde JL, Nagel E. Imaging in the management of ischemic cardiomyopathy: special focus on magnetic resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Jan 24;59(4):359–70. - PubMed
-
- Kim RJ, Wu E, Rafael A et al. The use of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to identify reversible myocardial dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 16;343(20):1445–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

