Potential Thai medicinal plants for neurodegenerative diseases: A review focusing on the anti-glutamate toxicity effect
- PMID: 32670825
- PMCID: PMC7340876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.03.003
Potential Thai medicinal plants for neurodegenerative diseases: A review focusing on the anti-glutamate toxicity effect
Abstract
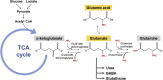
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDD) are a range of debilitating conditions of the brain involving progressive loss of neurons, many of which are still currently incurable despite enormous efforts on drug discovery and development in the past decade. As NDD is closely linked to old age, the rapid worldwide growth in the aging population contributes to an increasing number of people with one of these incurable diseases and therefore it is considered a significant global health issue. There is an urgent need for novel effective treatments for NDD, and many new research strategies are centered on traditional medicine as an alternative or complementary solution. Several previous findings have suggested that glutamate toxicity drives neurodegeneration in many NDD, and the medicinal plants with anti-glutamate toxicity properties can be potentially used for their treatment. In order to obtain data relating to natural products against glutamate toxicity, six candidate plant species of Thailand were identified. Studies utilizing these herbs were searched for using the herb name (Latin and common names) along with the term "glutamate" in the following databases across all available years: PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. This review emphasizes the importance of glutamate toxicity in NDD and summarizes individual plants and their active constituents with the mechanism of action against glutamate toxicity-mediated neuronal cell death that could be a promising resource for future NDD therapy.
Taxonomy classification by evise: Alzheimer's disease, Neurodegenerative diseases, Cell culture, Molecular Biology, Traditional herbal medicine, Oxidative stress, Glutamate neurotransmitter.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Glutamate; Herbal medicine; Neuroprotective; Neurotoxicity; Oxidative stress; Plant extract; Traditional medicine.
© 2020 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Robinson M.M., Zhang X. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2011. The World Medicines Situation 2011, Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges; pp. 1–12.
-
- De Luca V., Salim V., Atsumi S.M., Yu F. Mining the biodiversity of plants: a revolution in the making. Science. 2012;336(6089):1658–1661. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
