Treatment of invasive Paget's disease of the vulva in pregnancy: A case report
- PMID: 32671169
- PMCID: PMC7340971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gore.2020.100602
Treatment of invasive Paget's disease of the vulva in pregnancy: A case report
Abstract
•Invasive adenocarcinoma of the vulva arising from extramammary Paget's disease is possible in women of child-bearing age.•Radical vulvectomy, sentinel lymph node biopsy, and inguinal lymphadenectomy are safe and feasible during pregnancy.•Chemotherapy may be used as adjuvant therapy for vulvar adenocarcinoma during pregnancy when radiation is contraindicated.•Primary cesarean delivery may be considered for pregnant women with recent vulvar surgery.•Trastuzumab may be considered for maintenance therapy of Her2/Neu positive vulvar cancer in postpartum women.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
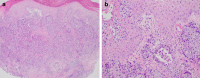
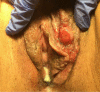
References
-
- Amant F., Nooij L., Annibali D., van Rompuy A.S., Han S., van den Bulck H. Brief report on 3-weekly paclitaxel carboplatin efficacy in locally advanced or metastatic squamous vulvar cancer. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2018;83(6):620–626. - PubMed
-
- Amant F., Berveiller P., Boere I.A., Cardonick E., Fruscio R., Fumagalli M. Gynecologic cancers in pregnancy: guidelines based on a third international consensus meeting. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30(10):1601–1612. - PubMed
-
- Ichiyama T., Gomi D., Fukushima T., Kobayashi T., Sekiguchi N., Sakamoto A. Successful and long-term response to trastuzumab plus paclitaxel combination therapy in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive extramammary Paget's disease: A case report and review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017;7(5):763–766. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsuo K., Whitman S.A., Blake E.A., Conturie C.L., Ciccone M.A., Jung C.E. Feto-maternal outcome of pregnancy complicated by vulvar cancer: a systematic review of literature. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2014;179:216–223. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
