Horizontal gene transfer rate is not the primary determinant of observed antibiotic resistance frequencies in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 32671212
- PMCID: PMC7314567
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz6137
Horizontal gene transfer rate is not the primary determinant of observed antibiotic resistance frequencies in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
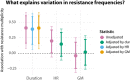
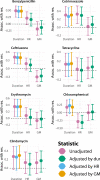
The extent to which evolution is constrained by the rate at which horizontal gene transfer (HGT) allows DNA to move between genetic lineages is an open question, which we address in the context of antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. We analyze microbiological, genomic, and epidemiological data from the largest-to-date sequenced pneumococcal carriage study in 955 infants from a refugee camp on the Thailand-Myanmar border. Using a unified framework, we simultaneously test prior hypotheses on rates of HGT and a key evolutionary covariate (duration of carriage) as determinants of resistance frequencies. We conclude that in this setting, there is little evidence of HGT playing a major role in determining resistance frequencies. Instead, observed resistance frequencies are best explained as the outcome of selection acting on a pool of variants, irrespective of the rate at which resistance determinants move between genetic lineages.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes that frequently colonise the human nasopharynx are common recipients of penicillin-binding protein gene fragments from Streptococcus mitis.Microb Genom. 2021 Sep;7(9):000622. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000622. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 34550067 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of antibiotic resistance is linked to any genetic mechanism affecting bacterial duration of carriage.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 31;114(5):1075-1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617849114. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28096340 Free PMC article.
-
Dense genomic sampling identifies highways of pneumococcal recombination.Nat Genet. 2014 Mar;46(3):305-309. doi: 10.1038/ng.2895. Epub 2014 Feb 9. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 24509479 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of genome evolution of Streptococcus.Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Jul;33:334-42. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.11.007. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 25461843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Horizontal gene transfer: a critical view.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Aug 19;100(17):9658-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1632870100. Epub 2003 Aug 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12902542 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial evolution during human infection: Adapt and live or adapt and die.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Sep 9;17(9):e1009872. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009872. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34499699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasive Pneumococcal Strain Distributions and Isolate Clusters Associated With Persons Experiencing Homelessness During 2018.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 15;72(12):e948-e956. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1680. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33150366 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying the effects of antibiotic resistance and within-host competition on strain fitness in Streptococcus pneumoniae.PLoS Biol. 2025 Aug 5;23(8):e3003300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003300. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40763153 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and horizontal gene transfer underlie microdiversity-level heterogeneity in resistance gene fate during wastewater treatment.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 26;15(1):5412. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49742-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38926391 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and interpopulation transposition of mobile genetic elements driven by antibiotic selection.Nat Ecol Evol. 2022 May;6(5):555-564. doi: 10.1038/s41559-022-01705-2. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Nat Ecol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35347261
References
-
- O’Malley M. A., ‘Everything is everywhere: but the environment selects’: Ubiquitous distribution and ecological determinism in microbial biogeography. Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 39, 314–325 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Croucher N. J., Harris S. R., Fraser C., Quail M. A., Burton J., van der Linden M., McGee L., von Gottberg A., Song J. H., Ko K. S., Pichon B., Baker S., Parry C. M., Lambertsen L. M., Shahinas D., Pillai D. R., Mitchell T. J., Dougan G., Tomasz A., Klugman K. P., Parkhill J., Hanage W. P., Bentley S. D., Rapid pneumococcal evolution in response to clinical interventions. Science 331, 430–434 (2011). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chewapreecha C., Harris S. R., Croucher N. J., Turner C., Marttinen P., Cheng L., Pessia A., Aanensen D. M., Mather A. E., Page A. J., Salter S. J., Harris D., Nosten F., Goldblatt D., Corander J., Parkhill J., Turner P., Bentley S. D., Dense genomic sampling identifies highways of pneumococcal recombination. Nat. Genet. 46, 305–309 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- MacLean R. C., San Millan A., The evolution of antibiotic resistance. Science 365, 1082–1083 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

