The identification of differentially expressed genes in male and female gametophytes of simple thalloid liverwort Pellia endiviifolia sp. B using an RNA-seq approach
- PMID: 32671488
- PMCID: PMC7363739
- DOI: 10.1007/s00425-020-03424-z
The identification of differentially expressed genes in male and female gametophytes of simple thalloid liverwort Pellia endiviifolia sp. B using an RNA-seq approach
Abstract
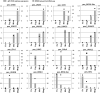
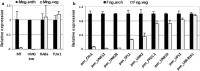
This study shows differences in gene expression between male and female gametophytes of the simple thalloid liverwort with a distinction between the vegetative and reproductive phases of growth. Pellia endiviifolia is a simple thalloid liverwort that, together with hornworts and mosses, represents the oldest living land plants. The limited taxon sampling for genomic and functional studies hampers our understanding of processes governing evolution of these plants. RNA sequencing represents an attractive way to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of non-model species development. In the present study, RNA-seq was used to profile the differences in gene expression between P. endiviifolia male and female gametophytes, with a distinction between the vegetative and reproductive phases of growth. By comparison of the gene expression profiles from individuals producing sex organs with the remaining thalli types, we have determined a set of genes whose expression might be important for the development of P. endiviifolia reproductive organs. The selected differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were categorized into five main pathways: metabolism, genetic information processing, environmental information processing, cellular processes, and organismal systems. A comparison of the obtained data with the Marchantia polymorpha transcriptome resulted in the identification of genes exhibiting a similar expression pattern during the reproductive phase of growth between members of the two distinct liverwort classes. The common expression profile of 87 selected genes suggests a common mechanism governing sex organ development in both liverwort species. The obtained RNA-seq results were confirmed by RT-qPCR for the DEGs with the highest differences in expression level. Five Pellia-female-specific and two Pellia-male-specific DEGs showed enriched expression in archegonia and antheridia, respectively. The identified genes are promising candidates for functional studies of their involvement in liverwort sexual reproduction.
Keywords: Antheridia; Archegonia; Bryophytes; Generative phase; Thalli; Vegetative phase.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Female-specific gene expression in dioecious liverwort Pellia endiviifolia is developmentally regulated and connected to archegonia production.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Jun 17;14:168. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-168. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24939387 Free PMC article.
-
Novel genes specifically expressed during the development of the male thalli and antheridia in the dioecious liverwort Pellia endiviifolia.Gene. 2011 Oct 1;485(1):53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Gene. 2011. PMID: 21712080
-
The liverwort Pellia endiviifolia shares microtranscriptomic traits that are common to green algae and land plants.New Phytol. 2015 Apr;206(1):352-367. doi: 10.1111/nph.13220. Epub 2014 Dec 19. New Phytol. 2015. PMID: 25530158 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, conservation, and function of miRNA in liverworts.J Exp Bot. 2022 Jul 16;73(13):4528-4545. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac098. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35275209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vegetative and reproductive innovations of early land plants: implications for a unified phylogeny.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Jun 29;355(1398):769-93. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0615. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 10905609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of gametangia and gametangiophore initiation in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha.Plant Reprod. 2021 Dec;34(4):297-306. doi: 10.1007/s00497-021-00419-y. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Plant Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34117568 Review.
-
Identifying Genes Associated with Female Flower Development of Phellodendron amurense Rupr. Using a Transcriptomics Approach.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;14(3):661. doi: 10.3390/genes14030661. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980934 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis and Identification of a Female-Specific SSR Marker in Pistacia chinensis Based on Illumina Paired-End RNA Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 7;13(6):1024. doi: 10.3390/genes13061024. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroniz-Crespo M, Nunez-Olivera E, Martinez-Abaigar J, Tomas R (2004) A survey of the distribution of UV-absorbing compounds in aquatic bryophytes from a mountain stream. The Bryologist 107:202–208. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3244845
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

