Effects of two kinds of fishery drugs on the expressions of GAD and GABA-T mRNA in crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio)
- PMID: 32671610
- PMCID: PMC7584538
- DOI: 10.1007/s10695-020-00847-z
Effects of two kinds of fishery drugs on the expressions of GAD and GABA-T mRNA in crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio)
Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of difloxacin (DIF) and avermectin (AVM) on glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) in different tissues of crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). After the treatments of DIF and AVM, the mRNA expressions of GAD and GABA-T in different tissues were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). The results showed that the mRNA expressions of GAD65, GAD67, and GABA-T in the telencephalon (Tel), mesencephalon (Mes), cerebella (Cer), and medulla oblongata (Med) were downregulated significantly with the safe dose (SD, 20 mg/kg) of DIF (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). While the expressions of GAD65 and GAD67 in the kidney at 12 h had strikingly upregulated to 13.81 ± 1.06** and 150.67 ± 12.85** times. Treated with the lethal dose of 50% (LD50, 2840 mg/kg b. W.) of DIF, the mRNA expressions of GAD65, GAD67, and GABA-T in all tissues were increased significantly (P < 0.01). The results of AVM group showed that the mRNA expressions of GAD65, GAD67, and GABA-T both in the central and peripheral tissues were all remarkably downregulated at the safe concentration (SC, 0.0039 mg/L) and the lethal concentration of 50% (LC50, 0.039 mg/L), except for the mRNA inhibitions of GAD65, GAD67, and GABA-T in the muscle at 2 h which sharply downregulated to 0.20 ± 0.02ΔΔ × 10-2, 0.57 ± 0.06ΔΔ × 10-1 and 0.44 ± 0.02ΔΔ × 10-1, respectively (P < 0.01).
Keywords: Avermectin; Difloxacin; GABA-transaminase; Gamma-aminobutyric acid; Glutamate decarboxylase.
Figures


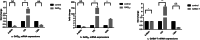
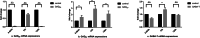
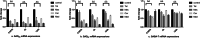
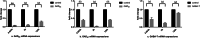

References
-
- Arafa N, Rawi MS, Mubarak SM, Abdullah S. Exploration of the neurotoxicity of ciprofloxcin or gatifloxacin single dose in rat cortex and hippocampus. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;9:65–73. doi: 10.5897/AJPP2014.4231. - DOI
-
- Cornejo I, Andrini O, Niemeyer MI, Marabolí V, González-Nilo FD, Teulon J, Sepúlveda FV, Cid LP. Identification and functional expression of a glutamate- and avermectin-gated chloride channel from Caligus rogercresseyi, a southern hemisphere sea louse affecting farmed fish. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004402. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

