Effect of COVID-19 on Tuberculosis Notification, South Korea
- PMID: 32672531
- PMCID: PMC7510739
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2610.202782
Effect of COVID-19 on Tuberculosis Notification, South Korea
Abstract
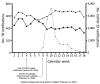
After South Korea raised its infectious disease alert to the highest level in response to coronavirus disease emergence, tuberculosis notification during the first 18 weeks of 2020 decreased significantly from the same period for each year during 2015-2019. Adequate measures to diagnose, control, and prevent tuberculosis need to be maintained.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; South Korea; bacteria; coronavirus disease; respiratory diseases; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; tuberculosis; tuberculosis and other mycobacteria; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Public Health Weekly Report [in Korean] [cited 2020 Jul 1]. https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30501000000&bid=0031&cg_code=C04
-
- Pai M. COVID-19 coronavirus and tuberculosis: we need a damage control plan. Forbes. 2020. Mar 17 [cited 2020 Jul 1]. https://www.forbes.com/sites/madhukarpai/2020/03/17/covid-19-and-tubercu...
-
- Brodersen KH, Gallusser F, Koehler J, Remy N, Scott SL. Inferring causal impact using Bayesian structural time-series models. Ann Appl Stat. 2015;9:247–74. 10.1214/14-AOAS788 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

