Recent advances in bioelectronics chemistry
- PMID: 32672777
- PMCID: PMC7674226
- DOI: 10.1039/d0cs00333f
Recent advances in bioelectronics chemistry
Abstract
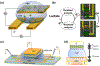
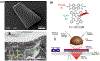
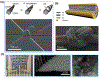
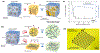
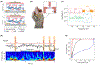
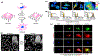
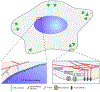
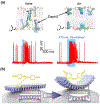
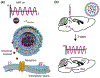
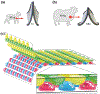
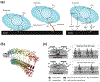
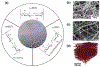
Research in bioelectronics is highly interdisciplinary, with many new developments being based on techniques from across the physical and life sciences. Advances in our understanding of the fundamental chemistry underlying the materials used in bioelectronic applications have been a crucial component of many recent discoveries. In this review, we highlight ways in which a chemistry-oriented perspective may facilitate novel and deep insights into both the fundamental scientific understanding and the design of materials, which can in turn tune the functionality and biocompatibility of bioelectronic devices. We provide an in-depth examination of several developments in the field, organized by the chemical properties of the materials. We conclude by surveying how some of the latest major topics of chemical research may be further integrated with bioelectronics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

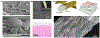
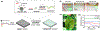
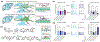
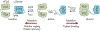
References
-
- Chortos A, Liu J and Bao Z, Nature Materials, 2016, 15, 937–950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

