Nivolumab versus everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Updated results with long-term follow-up of the randomized, open-label, phase 3 CheckMate 025 trial
- PMID: 32673417
- PMCID: PMC8415096
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.33033
Nivolumab versus everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Updated results with long-term follow-up of the randomized, open-label, phase 3 CheckMate 025 trial
Abstract
Background: CheckMate 025 has shown superior efficacy for nivolumab over everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) along with improved safety and tolerability. This analysis assesses the long-term clinical benefits of nivolumab versus everolimus.
Methods: The randomized, open-label, phase 3 CheckMate 025 trial (NCT01668784) included patients with clear cell aRCC previously treated with 1 or 2 antiangiogenic regimens. Patients were randomized to nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks) or everolimus (10 mg once a day) until progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). The secondary endpoints were the confirmed objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), safety, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL).
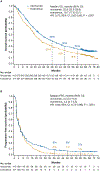
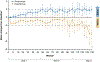
Results: Eight hundred twenty-one patients were randomized to nivolumab (n = 410) or everolimus (n = 411); 803 patients were treated (406 with nivolumab and 397 with everolimus). With a minimum follow-up of 64 months (median, 72 months), nivolumab maintained an OS benefit in comparison with everolimus (median, 25.8 months [95% CI, 22.2-29.8 months] vs 19.7 months [95% CI, 17.6-22.1 months]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.73; 95% CI, 0.62-0.85) with 5-year OS probabilities of 26% and 18%, respectively. ORR was higher with nivolumab (94 of 410 [23%] vs 17 of 411 [4%]; P < .001). PFS also favored nivolumab (HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72-0.99; P = .0331). The most common treatment-related adverse events of any grade were fatigue (34.7%) and pruritus (15.5%) with nivolumab and fatigue (34.5%) and stomatitis (29.5%) with everolimus. HRQOL improved from baseline with nivolumab but remained the same or deteriorated with everolimus.
Conclusions: The superior efficacy of nivolumab over everolimus is maintained after extended follow-up with no new safety signals, and this supports the long-term benefits of nivolumab monotherapy in patients with previously treated aRCC.
Lay summary: CheckMate 025 compared the effects of nivolumab (a novel immunotherapy) with those of everolimus (an older standard-of-care therapy) for the treatment of advanced kidney cancer in patients who had progressed on antiangiogenic therapy. After 5 years of study, nivolumab continues to be better than everolimus in extending the lives of patients, providing a long-lasting response to treatment, and improving quality of life with a manageable safety profile. The results demonstrate that the clinical benefits of nivolumab versus everolimus in previously treated patients with advanced kidney cancer continue in the long term.
Keywords: CheckMate 025; advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC); everolimus; immune checkpoint inhibitor; nivolumab; previously treated.
© 2020 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I, Immediate Family Member; Inst, Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript.
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb. Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Exelixis.
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai, Bayer.
Figures




References
-
- OPDIVO (nivolumab). [package insert]. Bristol Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ, USA; 2019.

