Exosome-transmitted linc00852 associated with receptor tyrosine kinase AXL dysregulates the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma
- PMID: 32673448
- PMCID: PMC7476833
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3303
Exosome-transmitted linc00852 associated with receptor tyrosine kinase AXL dysregulates the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: Receptor tyrosine kinase AXL has been found to be highly expressed in osteosarcoma and positively associated with poor prognosis. There are tumor groups with high or low AXL expression, which had different capabilities of invading vessels and forming distal metastases. Exosome-transmitted lncRNA may be transferred intercellularly to promote tumor cells' proliferation and invasion.
Methods: Exosomes were detected by electron microscopy, particle size analysis, and western blotting. High-throughput sequencing helped to find the highest differentially expressed lncRNA in AXL-associated exosomes. Clone formation, wound healing, transwell assay, and xenograft model in nude mice were performed to evaluate cells' proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Lentiviral transfection was used to up- or down-regulate the lncRNA levels in cell lines. Luciferase reporter assay and RNA FISH etchelped to indicate the molecular mechanisms. The results in the cell lines were proved in the osteosarcoma tissues with clinical analysis.
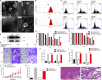
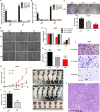
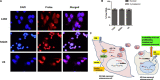
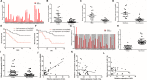
Results: The exosomes derived from donor cells with high AXL expression could promote the proliferation and invasion and upregulate AXL expression of the receiver cells with low AXL. Linc00852 was the highest differentially expressed lncRNA in AXL-associated exosomes and was also regulated by AXL expression. Although the mechanisms of linc00852 in nucleus were unrevealed, it could upregulate AXL expression partly by competitively binding to miR-7-5p. The AXL-exosome-linc00852-AXL positive feedback loop might exist between the donor cells and the receiver cells. Clinically, linc00852 was significantly highly expressed in osteosarcoma tissues and positively associated with tumor volumes and metastases, which was also obviously related with AXL mRNA expression.
Conclusion: AXL-associated exosomal linc00852 up-regulated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells, which would be considered as a new tumor biomarker and a special therapeutic target for osteosarcoma.
Keywords: AXL; exosome; invasion; linc00852; osteosarcoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
It has been submitted with the full knowledge and approval of the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat‐sen University. All authors have significantly contributed and are in agreement with the content of the final manuscript. The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Figures


References
-
- Jiang N, Wang X, Xie X, et al. lncRNA DANCR promotes tumor progression and cancer stemness features in osteosarcoma by upregulating AXL via miR‐33a‐5p inhibition. Cancer Lett. 2017;405:46‐55. - PubMed
-
- Antony J, Huang RY. AXL‐driven EMT state as a targetable conduit in cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77(14):3725‐3732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

