The Cytokine TGF-β Induces Interleukin-31 Expression from Dermal Dendritic Cells to Activate Sensory Neurons and Stimulate Wound Itching
- PMID: 32673566
- PMCID: PMC7362873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.023
The Cytokine TGF-β Induces Interleukin-31 Expression from Dermal Dendritic Cells to Activate Sensory Neurons and Stimulate Wound Itching
Abstract
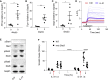
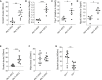
Cutaneous wound healing is associated with the unpleasant sensation of itching. Here we investigated the mechanisms underlying this type of itch, focusing on the contribution of soluble factors released during healing. We found high amounts of interleukin 31 (IL-31) in skin wound tissue during the peak of itch responses. Il31-/- mice lacked wound-induced itch responses. IL-31 was released by dermal conventional type 2 dendritic cells (cDC2s) recruited to wounds and increased itch sensory neuron sensitivity. Transfer of cDC2s isolated from late-stage wounds into healthy skin was sufficient to induce itching in a manner dependent on IL-31 expression. Addition of the cytokine TGF-β1, which promotes wound healing, to dermal DCs in vitro was sufficient to induce Il31 expression, and Tgfbr1f/f CD11c-Cre mice exhibited reduced scratching and decreased Il31 expression in wounds in vivo. Thus, cDC2s promote itching during skin would healing via a TGF-β-IL-31 axis with implications for treatment of wound itching.
Keywords: dermal dendritic cells; interleukin-31; itch; neuro-immune interaction; transforming growth factor beta; wound healing.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Scratching Beyond the Surface of Itchy Wounds.Immunity. 2020 Aug 18;53(2):235-237. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.016. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32814020
References
-
- Arai I., Tsuji M., Takeda H., Akiyama N., Saito S. A single dose of interleukin-31 (IL-31) causes continuous itch-associated scratching behaviour in mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2013;22:669–671. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft G.S., Yang X., Glick A.B., Weinstein M., Letterio J.L., Mizel D.E., Anzano M., Greenwell-Wild T., Wahl S.M., Deng C., Roberts A.B. Mice lacking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999;1:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft G.S., Lei K., Jin W., Longenecker G., Kulkarni A.B., Greenwell-Wild T., Hale-Donze H., McGrady G., Song X.Y., Wahl S.M. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor mediates non-redundant functions necessary for normal wound healing. Nat. Med. 2000;6:1147–1153. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos S., Stojadinovic O., Golinko M.S., Brem H., Tomic-Canic M. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16:585–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

