Effects of Health Information Dissemination on User Follows and Likes during COVID-19 Outbreak in China: Data and Content Analysis
- PMID: 32674510
- PMCID: PMC7399940
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17145081
Effects of Health Information Dissemination on User Follows and Likes during COVID-19 Outbreak in China: Data and Content Analysis
Abstract
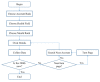
Background: COVID-19 has greatly attacked China, spreading in the whole world. Articles were posted on many official WeChat accounts to transmit health information about this pandemic. The public also sought related information via social media more frequently. However, little is known about what kinds of information satisfy them better. This study aimed to explore the characteristics of health information dissemination that affected users' information behavior on WeChat. Methods: Two-wave data were collected from the top 200 WeChat official accounts on the Xigua website. The data included the change in the number of followers and the total number of likes on each account in a 7-day period, as well as the number of each type of article and headlines about coronavirus. It was used to developed regression models and conduct content analysis to figure out information characteristics in quantity and content. Results: For nonmedical institution accounts in the model, report and story types of articles had positive effects on users' following behaviors. The number of headlines on coronavirus positively impacts liking behaviors. For medical institution accounts, report and science types had a positive effect, too. In the content analysis, several common characteristics were identified. Conclusions: Characteristics in terms of the quantity and content in health information dissemination contribute to users' information behavior. In terms of the content in the headlines, via coding and word frequency analysis, organizational structure, multimedia applications, and instructions-the common dimension in different articles-composed the common features in information that impacted users' liking behaviors.
Keywords: characteristic; content analysis; health information dissemination; novel coronavirus; official account; regression model; users’ information behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- WHO . Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report-141. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. [(accessed on 9 June 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Fox C.S., Barry K., Colbert J. Importance of Social Media Alongside Traditional Medical Publications. Circulation. 2016;133:1978–1983. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020303. - DOI
-
- CSM Media Research . Expectation Survey Report on Users’ Media Consumption and Use during the Epidemic. CSM Media Research; HongKong, China: 2020. [(accessed on 9 June 2020)]. Available online: http://www.csm.com.cn/Content/2020/02-25/1015314370.html.
-
- Zhao H. Wechat Annual Data Report in 2019. Fast Technology; St Mellons CF3, GB, USA: 2020. [(accessed on 9 June 2020)]. Available online: http://news.mydrivers.com/1/666/666552.htm.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

