The Use of Factorial Design and Simplex Optimization to Improve Analytical Performance of In Situ Film Electrodes
- PMID: 32674513
- PMCID: PMC7411898
- DOI: 10.3390/s20143921
The Use of Factorial Design and Simplex Optimization to Improve Analytical Performance of In Situ Film Electrodes
Abstract
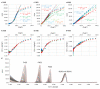
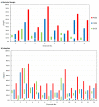
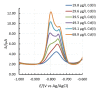
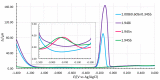
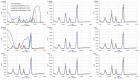
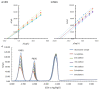
This work presents a systematic approach to determining the significance of the individual factors affecting the analytical performance of in-situ film electrode (FE) for the determination of Zn(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II). Analytical parameters were considered simultaneously, where the lowest limit of quantification, the widest linear concentration range, and the highest sensitivity, accuracy, and precision of the method evidenced a better analytical method. Significance was evaluated by means of a fractional factorial (experimental) design using five factors, i.e., the mass concentrations of Bi(III), Sn(II), and Sb(III), to design the in situ FE, the accumulation potential, and the accumulation time. Next, a simplex optimization procedure was employed to determine the optimum conditions for these factors. Such optimization of the in situ FE showed significant improvement in analytical performance compared to the in situ FEs in the initial experiments and compared to pure in situ FEs (bismuth-film, tin-film, and antimony-film electrodes). Moreover, using the optimized in situ FE electrode, a possible interference effect was checked for different species and the applicability of the electrode was demonstrated for a real tap water sample.
Keywords: factorial design; optimization; simplex; trace heavy metals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study of Nafion-coated bismuth-film electrodes for the determination of trace metals by anodic stripping voltammetry.Analyst. 2004 Nov;129(11):1082-90. doi: 10.1039/b404978k. Epub 2004 Sep 3. Analyst. 2004. PMID: 15508038
-
Sensitive determination of trace Cd(ii) and Pb(ii) in soil by an improved stripping voltammetry method using two different in situ plated bismuth-film electrodes based on a novel electrochemical measurement system.RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 30;8(10):5079-5089. doi: 10.1039/c7ra12767g. eCollection 2018 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542410 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Bi(iii)-to-metal ion concentration ratios on stripping voltammetric response of bismuth-film glassy carbon electrodes.RSC Adv. 2024 Dec 12;14(53):39361-39371. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07034h. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39670157 Free PMC article.
-
Antimony film screen-printed carbon electrode for stripping analysis of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Cu(II) in natural samples.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 15;855:34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25542087
-
Reusability of SPE and Sb-modified SPE Sensors for Trace Pb(II) Determination.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 15;18(11):3976. doi: 10.3390/s18113976. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30445794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Švancara I., Prior C., Hočevar S.B., Wang J. A Decade with Bismuth-Based Electrodes in Electroanalysis. Electroanalysis. 2010;22:1405–1420. doi: 10.1002/elan.200970017. - DOI
-
- Serrano N., Díaz-Cruz J.M., Ariño C., Esteban M. Antimony-Based electrodes for analytical determinations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016;77:203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.011. - DOI
-
- Pauliukaite R., Metelka R., Švancara I., Królicka A., Bobrowski A., Norkus E., Kalcher K., Vytřas K. Screen-Printed carbon electrodes bulk-modified with Bi2O3 OR Sb2O3 for trace determination of some heavy metals. Sci. Pap. Univ. Pardubic. Ser. A. 2004;10:47–58.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

