Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Update on diagnosis and management
- PMID: 32675143
- PMCID: PMC7385768
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0232
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Update on diagnosis and management
Abstract
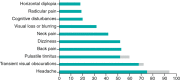
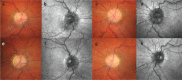
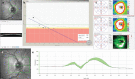
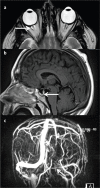
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is a condition of raised intracranial pressure of unknown cause. Features include new onset headache, which is frequently non-specific; papilloedema is present, visual disturbances are common; and there may be sixth nerve palsy. Diagnosis includes brain imaging with venography to exclude structural causes and venous sinus thrombosis. Lumbar puncture reveals pressure greater than 250 mmCSF with normal constituents. Treatments aim to modify the disease, prevent permanent visual loss and manage headaches. These include weight loss. For those with rapid visual decline, urgent surgical intervention is essential. For most, this is a chronic condition characterised by significantly disabling headaches.
Keywords: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; headache; obesity; papilloedema; raised intracranial pressure.
© Royal College of Physicians 2020. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension.Clin Med (Lond). 2020 Sep;20(5):e138. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.Let.20.5.6. Clin Med (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32934058 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Markey KA, Mollan SP, Jensen RH, Sinclair AJ. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:78–91. - PubMed

