Clinical Conditions of Hospitalized Older Adult Patients and Their Outcomes in a Regional Referral Hospital in Southwestern Uganda
- PMID: 32676210
- PMCID: PMC7341388
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6830495
Clinical Conditions of Hospitalized Older Adult Patients and Their Outcomes in a Regional Referral Hospital in Southwestern Uganda
Abstract
Background: Recent advances in medicine have caused positive impact on the life expectancy of most countries, resulting in increased older adult population. Aging comes with a number of health challenges. This study investigated health conditions of older adults at admission and clinical outcomes in a regional referral hospital in southwestern Uganda.
Methods: A retrospective study reviewed clinical data of older adult patients admitted between January 2016 and December 2017. Demographic data, cause of admission, length, and outcomes of hospitalization are described.
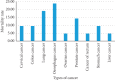
Results: Up to 813 patient files were reviewed. The patients had been hospitalized to emergency, 371 (45.6%); medical, 355 (43.7%); surgical, 84 (10.3%); psychiatry, 2 (0.3%); and obstetrics and gynecology, 1 (0.1%) wards. The majority, 427 (52.5%), of the patients were females. Cancer was the most common reason for hospitalization, 130/889 (14.6%), followed by stroke, 94/889 (10.6%); heart failure, 76/889 (8.6%); chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, 56/889 (6.3%); pneumonia, 47/889 (5.3%); and head injury, 45/889 (5.1%), whilst 560 (68.9%) of the hospitalized patients were discharged, 197 (24.2%) died, 18 (2.2%) were referred for advanced care, and 38 (4.7%) escaped from the facility. The emergency ward had the highest deaths, 101 (51.3%), then medical, 56 (28.4%), and surgical, 39 (19.8%), wards. Mortality of those who died was admitted with stroke, 30 (15.2%), cancer, 21 (10.7%), head injury, 16 (8.1%), heart failure, 14 (7.1%), sepsis, 14 (7.1%), and renal disease, 12 (6.1%). On average, patients were admitted for 5 days (IQR: 3-8).
Conclusions: The high proportion of mortality in this group is worrying and requires further investigations.
Copyright © 2020 Patrick Orikiriza et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Khole C. V., Soletti A., Mo J., et al. An Aging World: International Population Reports. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Appetite; 2016.
-
- UNDP. Help Age A. Ageing, Older Persons and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. New York, NY, USA: United Nations Publications; 2017.
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory Data Repository: Life Expectancy. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- He W., Goodkind D., Kowal P. An Aging World: 2015, International Population Reports. Suitland, MA, USA: United States Census Bureau; 2016.
-
- United Nations PDD of E and SA. World Aging Population. New York, NY, USA: United Nations New York; 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources