This is a preprint.
Structural basis for helicase-polymerase coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex
- PMID: 32676607
- PMCID: PMC7359531
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.07.08.194084
Structural basis for helicase-polymerase coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex
Update in
-
Structural Basis for Helicase-Polymerase Coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 Replication-Transcription Complex.Cell. 2020 Sep 17;182(6):1560-1573.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.033. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32783916 Free PMC article.
Abstract
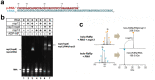
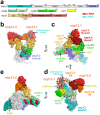
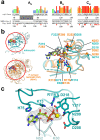
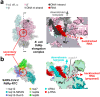
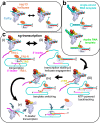
SARS-CoV-2 is the causative agent of the 2019-2020 pandemic. The SARS-CoV-2 genome is replicated-transcribed by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase holoenzyme (subunits nsp7/nsp82/nsp12) along with a cast of accessory factors. One of these factors is the nsp13 helicase. Both the holo-RdRp and nsp13 are essential for viral replication and are targets for treating the disease COVID-19. Here we present cryo-electron microscopic structures of the SARS-CoV-2 holo-RdRp with an RNA template-product in complex with two molecules of the nsp13 helicase. The Nidovirus-order-specific N-terminal domains of each nsp13 interact with the N-terminal extension of each copy of nsp8. One nsp13 also contacts the nsp12-thumb. The structure places the nucleic acid-binding ATPase domains of the helicase directly in front of the replicating-transcribing holo-RdRp, constraining models for nsp13 function. We also observe ADP-Mg2+ bound in the nsp12 N-terminal nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain, detailing a new pocket for anti-viral therapeutic development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
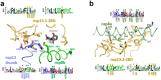
References
-
- Adams P.D., Afonine P.V., Bunkóczi G., Chen V.B., Davis I.W., Echols N., Headd J.J., Hung L.-W., Kapral G.J., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., et al. (2010). PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agostini M.L., Andres E.L., Sims A.C., Graham R.L., Sheahan T.P., Lu X., Smith E.C., Case J.B., Feng J.Y., Jordan R., et al. (2018). Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease. Mbio 9, e00221–18. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
