Visceral Adiposity and High Intramuscular Fat Deposition Independently Predict Critical Illness in Patients with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32677752
- PMCID: PMC7405187
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.22971
Visceral Adiposity and High Intramuscular Fat Deposition Independently Predict Critical Illness in Patients with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the association between adipose tissue distribution and severity of clinical course in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
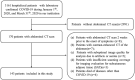
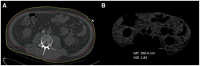
Methods: For this retrospective study, 143 hospitalized patients with confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who underwent an unenhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan between January 1, 2020, and March 30, 2020, were included. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify the risk factors associated with the severity of COVID-19 infection.
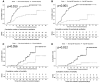
Results: There were 45 patients who were identified as critically ill. High visceral to subcutaneous adipose tissue area ratio (called visceral adiposity) (odds ratio: 2.47; 95% CI: 1.05-5.98, P = 0.040) and low mean attenuation of skeletal muscle (called high intramuscular fat [IMF] deposition) (odds ratio: 11.90; 95% CI: 4.50-36.14; P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for critical illness. Furthermore, visceral adiposity or high IMF deposition increased the risk of mechanical ventilation (P = 0.013, P < 0.001, respectively). High IMF deposition increased the risk of death (P = 0.012).
Conclusions: COVID-19 patients with visceral adiposity or high IMF deposition have higher risk for critical illness. Therefore, patients with abdominal obesity should be monitored more carefully when hospitalized.
© 2020 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case‐fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID‐19 in Italy. JAMA 2020;323:1775‐1776. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 721314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020;323:1239‐1242. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) Situation Report – 129. https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/2.... Updated May 28, 2020, Accessed May 28, 2020.
-
- Poston JT, Patel BK, Davis AM. Management of critically ill adults with COVID‐19. JAMA 2020;323:1839‐1841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

