A COVID-19 patient with multiple negative results for PCR assays outside Wuhan, China: a case report
- PMID: 32677909
- PMCID: PMC7364136
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05245-7
A COVID-19 patient with multiple negative results for PCR assays outside Wuhan, China: a case report
Abstract
Background: The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has become a public health emergency of major international concern. Real-time RT-PCR assays are recommended for diagnosis of COVID-19. Here we report a rare case of COVID-19 with multiple negative results for PCR assays outside Wuhan, China.
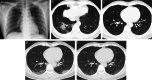
Case presentation: A 32-year old male was admitted to our hospital because of 6 days of unexplained fever on January 29, 2020. He had come from Wuhan city 10 days before admission. Five days before admission, no abnormality was noted in laboratory test, chest radiography, and nasopharyngeal swab test for the SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid. The patient was treated with ibuprofen for alleviating fever. On admission, chest computed tomography showed multiple ground-glass opacities in right lower lung field. COVID-19 was suspected. Three times of nasopharyngeal swab specimens were collected after admission. However, none of the specimens were positive. The patient was confirmed with COVID-19 after fifth SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid test. He was treated with lopinavir/ritonavir, recombinant human interferon alfa-2b inhalation, methylprednisolone. After 18 days of treatment, he was discharged with improved symptoms, lung lesions and negative results of nasopharyngeal swab.
Conclusion: This case reminds clinician that a patient with high clinical suspicion of COVID-19 but multiple negative RT-PCR result should not be taken out of isolation. A combination of patient's exposure history, clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and typical imaging findings plays a vital role in making preliminary diagnosis and guide early isolation and treatment. Repeat swab tests are helpful in diagnosis for this kind of patients.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; False negative; Real-time RT-PCR; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Yang Y, Yang M, Shen C, Wang F, Yuan J, Li J, Zhang M, Wang Z, Xing L. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections. medRxiv 2020. 10.1101/2020021120021493.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

