Correlation analysis between disease severity and clinical and biochemical characteristics of 143 cases of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study
- PMID: 32677918
- PMCID: PMC7364396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05242-w
Correlation analysis between disease severity and clinical and biochemical characteristics of 143 cases of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged in Wuhan and has quickly spread across the world. The mortality rate in critically ill patients with COVID-19 is high. This study analyzed clinical and biochemical parameters between mild and severe patients, helping to identify severe or critical patients early.
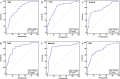
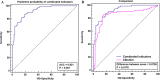
Methods: In this single center, cross-sectional study, 143 patients were included and divided to mild/moderate and sever/critical groups. Correlation between the disease criticality and clinical features and peripheral blood biochemical markers was analyzed. Cut-off values for critically ill patients were speculated through the ROC curve.
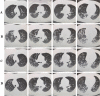
Results: Significantly, disease severity was associated with age (r = 0.458, P < 0.001), comorbidities (r = 0.445, P < 0.001), white cell count (r = 0.229, P = 0.006), neutrophil count (r = 0.238, P = 0.004), lymphocyte count (r = - 0.295, P < 0.001), albumin (r = - 0.603, P < 0.001), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (r = - 0.362, P < 0.001), serum potassium (r = - 0.237, P = 0.004), plasma glucose (r = 0.383, P < 0.001), total bilirubin (r = 0.340, P < 0.001), serum amyloid A (r = 0.58, P < 0.001), procalcitonin (r = 0.345, P < 0.001), C-reactive protein (r = 0.477, P < 0.001), lactate dehydrogenase (r = 0.548, P < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (r = 0.342, P < 0.001), alanine aminotransferase (r = 0.264, P = 0.001), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (r = 0.284, P = 0.001) and D-dimer (r = 0.477, P < 0.001) .
Conclusions: With the following parameters such as age > 52 years, C-reactive protein > 64.79 mg/L, lactate dehydrogenase > 245 U/L, D-dimer > 0.96 μg/mL, serum amyloid A > 100.02 mg/L, or albumin < 36 g/L, the progress of COVID-19 to critical stage should be closely observed and possibly prevented. Lymphocyte count, serum potassium, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and procalcitonin may also be a prognostic indicator.
Keywords: COVID-19; Correlation analysis; Prognostic indicator; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Notice on the novel coronavirus infection diagnosis and treatment plan (trial version sixth). In: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, editor. Beijing, 2020. Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/gfxwjj/list_5.shtml. Accessed 10 Mar 2020.
-
- National Health Commission Stroke Prevention and Control Engineering Expert Committee. Expert consensus on prevention and control of novel coronavirus infection in neurology (version first). In: National Health Commission Stroke Prevention and Control Engineering Expert Committee, editor. Beijing, 2020. Available from: http://www.sinosc.org/NewsInfo/News/NewsDetailWeb?Tid=2621. Accessed 10 Mar 2020.
-
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Hu S, Fan R, Liu Z, Yin X, Wang Q, Lv Q, Cai Z, Li H, Hu Y, et al: ACP risk grade: a simple mortality index for patients with confirmed or suspected severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 disease (COVID-19) during the early stage of outbreak in Wuhan, China. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.20.20025510v1 (2020). Accessed 23 Mar 2020. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

