SARS-CoV2 and pregnancy: An invisible enemy?
- PMID: 32678975
- PMCID: PMC7404619
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.13308
SARS-CoV2 and pregnancy: An invisible enemy?
Abstract
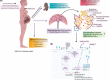
Coronavirus disease 2019 or COVID-19 is an emerging viral disease caused by a member of the betacoronavirus family, SARS-CoV-2. Since its' emergence in December 2019, it has rapidly caused close to half a million fatalities globally. Data regarding the impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy are limited. Here, we review pathological findings in placentas from women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 as well as information on pregnancy outcomes associated with related and highly pathogenic coronaviruses (ie, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-COV) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome, MERS). We present immune-inflammatory correlates of COVID-19 in pregnancy and review the role of the Renin Angiotensin System in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 in pregnancy. Greater understanding of the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in the placenta will yield important insight into potential therapeutic interventions for pregnant women with COVID-19.
Keywords: ACE2; AT1; COVID-19; placenta; pre-eclampsia; renin-angiotensin system.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous