The bio-mission of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of COVID-19: A brief look at potential therapeutic tactics
- PMID: 32679148
- PMCID: PMC7361088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118097
The bio-mission of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of COVID-19: A brief look at potential therapeutic tactics
Abstract
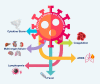
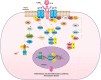
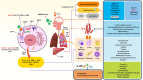
Interleukin-6 (IL-6), known as an inflammatory cytokine, can be involved in many innate and adaptive immune responses. The role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has recently received much more attention due to the spread of the virus and its pandemic potential. Cytokine storm is among the most critical pathological events in patients affected with coronaviruses (CoVs), i.e., severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and COVID-19, causing inflammation-induced lung injury and also occurring as a result of dysregulation of immune responses to the mentioned viruses. IL-6, along with some other inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1 beta (β), IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), as well as inflammatory chemokines, can significantly contribute to, fever, lymphopenia, coagulation, lung injury, and multi-organ failure (MOF). Therefore, researchers are to explore novel approaches to treat the disease through targeting of IL-6 and its receptors based on prior experience of other disorders. In this review article, the latest findings on the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, as well as therapeutic perspectives, were summarized and discussed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine storm; Immunopathogenesis; Interleukin-6; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Organization, W.H . 2020. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report; p. 67.
-
- del Rio C., Malani P.N. COVID-19—new insights on a rapidly changing epidemic. Jama. 2020;323.14:1339–1340. - PubMed
-
- Sahin A.R., et al. 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak: a review of the current literature. EJMO. 2020;4(1):1–7.
-
- Sun M., et al. Inhibitors of RAS might be a good choice for the therapy of COVID-19 pneumonia. Zhonghua jie he he hu xi za zhi= Zhonghua jiehe he huxi zazhi= Chinese journal of tuberculosis and respiratory diseases. 2020;43:E014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

