High Thrombus Burden in Patients With COVID-19 Presenting With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 32679155
- PMCID: PMC7833185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.07.022
High Thrombus Burden in Patients With COVID-19 Presenting With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) is thought to predispose patients to thrombotic disease. To date there are few reports of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) caused by type 1 myocardial infarction in patients with COVID-19.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to describe the demographic, angiographic, and procedural characteristics alongside clinical outcomes of consecutive cases of COVID-19-positive patients with STEMI compared with COVID-19-negative patients.
Methods: This was a single-center, observational study of 115 consecutive patients admitted with confirmed STEMI treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention at Barts Heart Centre between March 1, 2020, and May 20, 2020.
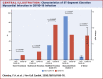
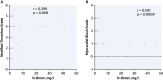
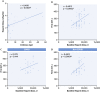
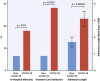
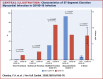
Results: Patients with STEMI presenting with concurrent COVID-19 infection had higher levels of troponin T and lower lymphocyte count, but elevated D-dimer and C-reactive protein. There were significantly higher rates of multivessel thrombosis, stent thrombosis, higher modified thrombus grade post first device with consequently higher use of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors and thrombus aspiration. Myocardial blush grade and left ventricular function were significantly lower in patients with COVID-19 with STEMI. Higher doses of heparin to achieve therapeutic activated clotting times were also noted. Importantly, patients with STEMI presenting with COVID-19 infection had a longer in-patient admission and higher rates of intensive care admission.
Conclusions: In patients presenting with STEMI and concurrent COVID-19 infection, there is a strong signal toward higher thrombus burden and poorer outcomes. This supports the need for establishing COVID-19 status in all STEMI cases. Further work is required to understand the mechanism of increased thrombosis and the benefit of aggressive antithrombotic therapy in selected cases.
Keywords: COVID-19; ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; primary percutaneous coronary intervention; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Unbearable Thrombus of COVID-19: Primary PCI, Thrombus, and COVID-19.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Sep 8;76(10):1177-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.07.027. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32883410 Free PMC article.
-
Pitfalls of Unfractionated Heparin Use During ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Patients With COVID-19 Infection.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Jan 5;77(1):104. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.090. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33413932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

