Sex is associated with differences in gut microbial composition and function in hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 32679299
- PMCID: PMC7749850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.046
Sex is associated with differences in gut microbial composition and function in hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background & aims: Altered microbiota can affect the gut-liver-brain axis in cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy (HE), but the impact of sex on these changes is unclear. We aimed to determine differences in fecal microbiota composition/functionality between men and women with cirrhosis and HE on differing treatments.
Methods: Cross-sectional stool microbiome composition (16s rRNA sequencing) and microbial functional analyses were performed in men and women with cirrhosis, and controls. Patients with HE on rifaximin+lactulose (HE-Rif), patients with HE on lactulose only (HE-Lac) and those with cirrhosis without HE (No-HE) were compared to controls using random forest classifier. Men and women were also compared.
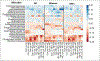
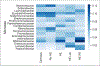
Results: A total of 761 individuals were included, 619 with cirrhosis (466 men, 153 women) and 142 controls (92 men, 50 women). Men were older and more frequently used proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), but model for end-stage liver disease score, No-HE (n = 319), HE-lac (n = 130) and HE-Rif (n = 170) proportions were similar. PPI/age-adjusted AUC of differentiation between controls vs. all cirrhosis, and controls vs. No-HE were higher within women than men, but the adjusted AUC for No-HE vs. HE-Rif was higher in men. Control vs. HE-Rif differentiation was similar across sexes. Men vs. women were different in all cirrhosis, No-HE and HE-Lac but not HE-Rif on PERMANOVA and AUC analyses. Autochthonous taxa decreased and pathobionts increased with disease progression regardless of sex. In men, Lactobacillaceae were higher in HE-Lac but decreased in HE-Rif, along with Veillonellaceae. Pathways related to glutamate and aromatic compound degradation were higher in men at all stages. Degradation of androstenedione, an estrogenic precursor, was lower in men vs. women in HE-Rif, likely enhancing feminization.
Conclusions: There are differences in gut microbial function and composition between men and women with cirrhosis, which could be implicated in differential responses to HE therapies. Further studies linking these differences to sex-specific outcomes are needed.
Lay summary: Patients with cirrhosis develop changes in their brain function, and men often develop feminization with disease progression. However, the interaction between sex, microbiota and disease severity is unclear. We found that as disease progressed in men, their microbial composition began to approach that observed in women, with changes in specific microbes that are associated with male hormone metabolism.
Keywords: Androgen; Artificial Intelligence; Cirrhosis; Lactobacillus; Lactulose; Random forest classifier; Rifaximin.
Copyright © 2020 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures


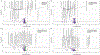
References
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60:715–735. - PubMed
-
- Stepanova M, Mishra A, Venkatesan C, Younossi ZM. In-hospital mortality and economic burden associated with hepatic encephalopathy in the United States from 2005 to 2009. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;10:1034–1041 e1031. - PubMed
-
- Iebba V, Guerrieri F, Di Gregorio V, Levrero M, Gagliardi A, Santangelo F, et al. Combining amplicon sequencing and metabolomics in cirrhotic patients highlights distinctive microbiota features involved in bacterial translocation, systemic inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy. Sci Rep 2018;8:8210. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allampati S, Duarte-Rojo A, Thacker LR, Patidar KR, White MB, Klair JS, et al. Diagnosis of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy Using Stroop EncephalApp: A Multicenter US-Based, Norm-Based Study. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:78–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

