Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32679347
- PMCID: PMC7347314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117019
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Objective: To report four patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who developed posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
Methods: Patient data was abstracted from medical records at Weill Cornell Medical Center.
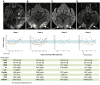
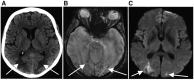
Results: Four patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and PRES were identified. The patients' ages ranged from 64 to 74 years, and two were women. All four patients were admitted to the hospital with acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring intensive care unit admission and mechanical ventilation. PRES was diagnosed after persistent confusion, lethargy, new focal neurological deficits, or seizures were noted, with evidence of seizures on electroencephalogram for two of the patients. Imaging confirmed the presence of cerebral vasogenic edema. All four patients had elevated blood pressure and renal injury in the days preceding PRES diagnosis, as well as evidence of systemic inflammation and systemic hypercoagulability. Symptoms of PRES improved with blood pressure control.
Conclusions: Our four cases demonstrate the occurrence of PRES in critically-ill patients with COVID-19. PRES should be considered in the differential for acute neurological deficits and seizures in this setting.
Keywords: COVID-19; Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Merkler has received personal fees for medicolegal consulting on stroke. Dr. Leifer has received personal fees for medicolegal consulting on Neurology. Dr. Navi serves as a DSMB member for the PCORI-funded TRAVERSE trial and has received personal fees for medicolegal consulting on stroke. Dr. Segal has received personal fees for medicolegal consulting on stroke. No other authors have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Hinchey J., Chaves C., Appignani B., Breen J., Pao L., Wang A., Pessin M.S., Lamy C., Mas J.L., Caplan L.R. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:494–500. - PubMed
-
- Fugate J.E., Rabinstein A.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(9):914–925. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

