Graduate medical education funding mechanisms, challenges, and solutions: A narrative review
- PMID: 32680622
- PMCID: PMC7308777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.06.007
Graduate medical education funding mechanisms, challenges, and solutions: A narrative review
Abstract
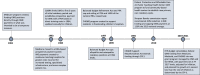
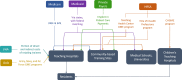
Background: With increased attention on the federal budget deficit, graduate medical education (GME) funding has in particular been targeted as a potential source of cost reduction. Reduced GME funding can further deteriorate the compensation of physicians during their residency training.
Methods: In order to understand the GME funding mechanisms and current challenges, as well as the value of the work accomplished by residents, we searched peer-reviewed, English language studies published between 2000 and 2019.
Results: Direct and indirect GME funding is intended to support resident reimbursement and the higher costs associated with supporting a teaching program. However, policy efforts have aimed to reduce federal funding for GME. Furthermore, evidence suggests that residents are inadequately compensated because their salaries do not reflect the number of hours worked and are not comparable to those of other medical staff.
Conclusions: Our review suggests that creative solutions are needed to diversify GME funding and improve resident compensation.
Keywords: Funding; Graduate medical education; Resident compensation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Congressional research service. Federal support for graduate medical education: an overview. https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R44376.pdf Published December 27, 2018. Accessed May 29, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

