Preprint Servers in Kidney Disease Research: A Rapid Review
- PMID: 32680914
- PMCID: PMC8011003
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03800320
Preprint Servers in Kidney Disease Research: A Rapid Review
Abstract
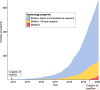
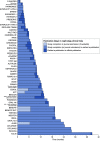
Preprint servers, such as arXiv and bioRxiv, have disrupted the scientific communication landscape by providing rapid access to research before peer review. medRxiv was launched as a free online repository for preprints in the medical, clinical, and related health sciences in 2019. In this review, we present the uptake of preprint server use in nephrology and discuss specific considerations regarding preprint server use in medicine. Distribution of kidney-related research on preprint servers is rising at an exponential rate. Survey of nephrology journals identified that 15 of 17 (88%) are publishing original research accepted submissions that have been uploaded to preprint servers. After reviewing 52 clinically impactful trials in nephrology discussed in the online Nephrology Journal Club (NephJC), an average lag of 300 days was found between study completion and publication, indicating an opportunity for faster research dissemination. Rapid review of papers discussing benefits and risks of preprint server use from the researcher, publisher, or end user perspective identified 53 papers that met criteria. Potential benefits of biomedical preprint servers included rapid dissemination, improved transparency of the peer review process, greater visibility and recognition, and collaboration. However, these benefits come at the risk of rapid spread of results not yet subjected to the rigors of peer review. Preprint servers shift the burden of critical appraisal to the reader. Media may be especially at risk due to their focus on "late-breaking" information. Preprint servers have played an even larger role when late-breaking research results are of special interest, such as during the global coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Coronavirus disease 2019 has brought both the benefits and risks of preprint servers to the forefront. Given the prominent online presence of the nephrology community, it is poised to lead the medicine community in appropriate use of preprint servers.
Keywords: Preprint; education; kidney disease; peer review; social media.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Cobb M: Preprints: Recall Nature’s nasty past. Nature 570: 36, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Berg JM, Bhalla N, Bourne PE, Chalfie M, Drubin DG, Fraser JS, Greider CW, Hendricks M, Jones C, Kiley R, King S, Kirschner MW, Krumholz HM, Lehmann R, Leptin M, Pulverer B, Rosenzweig B, Spiro JE, Stebbins M, Strasser C, Swaminathan S, Turner P, Vale RD, VijayRaghavan K, Wolberger C: Preprints for the life sciences. Science 352: 899–901, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Callaway E: bioRxiv preprint server gets cash boost from Chan Zuckerberg Initiative. Nature 545: 18, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Abdill RJ, Blekhman R: Rxivist.org: Sorting biology preprints using social media and readership metrics. PLoS Biol 17: e3000269, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

