Large-scale site-specific mapping of the O-GalNAc glycoproteome
- PMID: 32681153
- PMCID: PMC8620167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-020-0345-1
Large-scale site-specific mapping of the O-GalNAc glycoproteome
Abstract
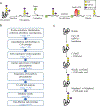
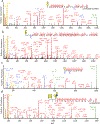
Protein glycosylation is one of the most common protein modifications. A major type of protein glycosylation is O-GalNAcylation, in which GalNAc-type glycans are attached to protein Ser or Thr residues via an O-linked glycosidic bond. O-GalNAcylation is thought to play roles in protein folding, stability, trafficking and protein interactions, and identification of the site-specific O-GalNAc glycoproteome is a crucial step toward understanding the biological significance of the modification. However, lack of suitable methodology, absence of consensus sequon of O-GalNAcylation sites and complex O-GalNAc glycan structures pose analytical challenges. We recently developed a mass spectrometry-based method called extraction of O-linked glycopeptides (EXoO) that enables large-scale mapping of site-specific mucin-type O-GalNAcylation sites. Here we provide a detailed protocol for EXoO, which includes seven stages of: (1) extraction and proteolytic digestion of proteins to peptides, (2) sequential guanidination and de-salting of peptides, (3) enrichment of glycopeptides, (4) solid-phase peptide conjugation and release of O-GalNAc glycopeptides using the OpeRATOR protease, (5) liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry analysis of O-GalNAc glycopeptides, (6) identification of O-GalNAc glycopeptides by database search and (7) quantification of O-GalNAc glycopeptides. Using this protocol, thousands of O-GalNAcylation sites from hundreds of glycoproteins with information regarding site-specific O-GalNAc glycan can be identified and quantified from complex samples. The protocol can be performed by a researcher with basic proteomics skills and takes about 4 d to complete.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gahmberg CG & Tolvanen M Why mammalian cell surface proteins are glycoproteins. Trends in biochemical sciences 21, 308–311 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

